Introduction
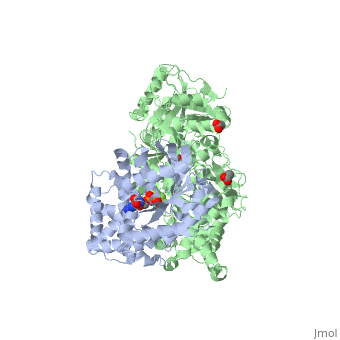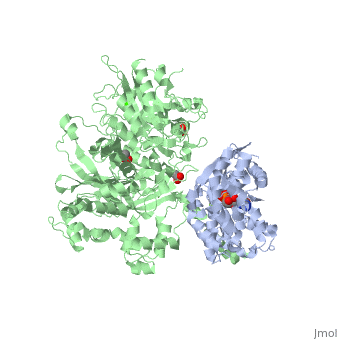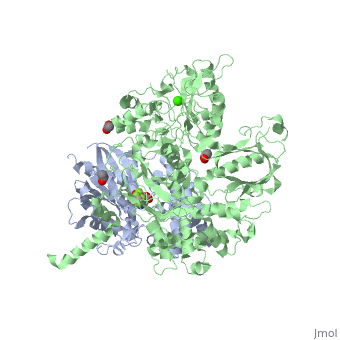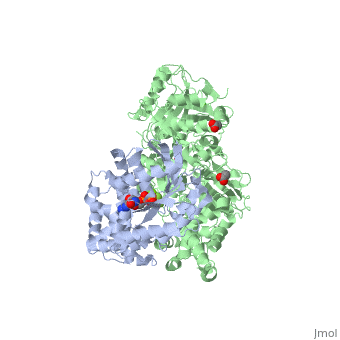
Phospholipase C (PLC) catalyzes the hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate [IP2] to the second messengers inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate [IP3] and diacylglycerol [DAG] in an essential step for the physiological action of many hormones, neurotransmitters, growth factors, and other extracellular stimuli. These cascades use signaling complexes consisting of G alpha subunits of the Gq family of heterotrimeric guanine nucleotide–binding proteins (G proteins) and PLC-beta isozymes (β1-4). Agonist-stimulated receptors increase exchange of guanosine diphosphate (GDP) for guanosine triphosphate (GTP) on Gαq. GTP-bound Gαq engages and activates PLC- β3, and PLC- β3 increases up to three orders of magnitude the rate of hydrolysis of GTP by its activating G protein. This is a unique mechanism when the PLC-β3 enzyme has the ability to terminate the Gαq protein signal in addition to being activated by it.[1] [2]
Structural highlights
This is a sample scene created with SAT to by Group, and another to make of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes.