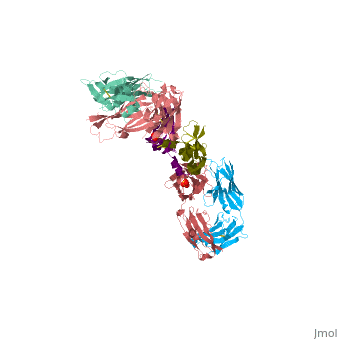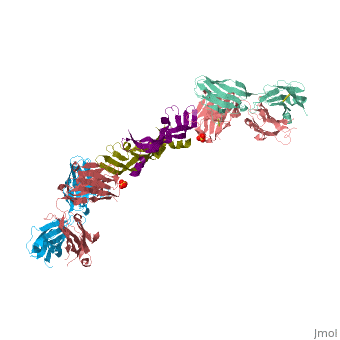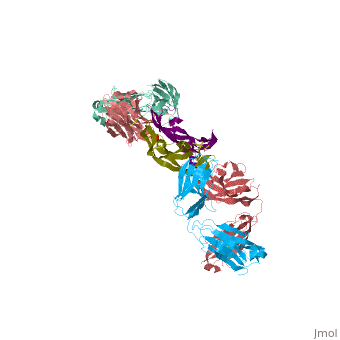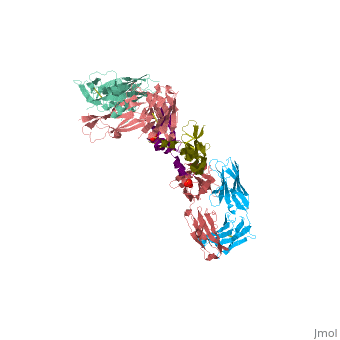1bj1
[1]
This is a default text for your page VEGF IN COMPLEX WITH A NEUTRALIZING ANTIBODY. Click above on edit this page to modify. Be careful with the < and > signs.
You may include any references to papers as in: the use of JSmol in Proteopedia [2] or to the article describing Jmol [3] to the rescue.
Backround
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), is a signal protein produced by cells that stimulates vasculogenesis and angiogenesis. It is part of the system that restores the oxygen supply to tissues when blood circulation is inadequate.
VEGF's normal function is to create new blood vessels during embryonic development, new blood vessels after injury, muscle following exercise, and new vessels (collateral circulation) to bypass blocked vessels.
When VEGF is overexpressed, it can contribute to disease. Solid cancers cannot grow beyond a limited size without an adequate blood supply; cancers that can express VEGF are able to grow and metastasize. Overexpression of VEGF can cause vascular disease in the retina of the eye and other parts of the body. Drugs such as bevacizumab and ranibizumab can inhibit VEGF and control or slow those diseases.
VEGF are important signaling proteins involved in both vasculogenesis (the de novo formation of the embryonic circulatory system) and angiogenesis (the growth of blood vessels from pre-existing vasculature).
anti-angiogenic treatment through inhibition of receptor activation by VEGF might have important therapeutic applications in diseases such as diabetic retinopathy and cancer. A neutralizing anti- VEGF antibody shown to suppress tumor growth in an in vivo murine model has been used as the basis for production of a humanized version.
Monoclonal antibodies (mAb or moAb) are monospecific antibodies that are made by identical immune cells that are all clones of a unique parent cell, in contrast to polyclonal antibodies which are made from several different immune cells. Monoclonal antibodies have monovalent affinity, in that they bind to the same epitope.
Given almost any substance, it is possible to produce monoclonal antibodies that specifically bind to that substance; they can then serve to detect or purify that substance. This has become an important tool in biochemistry, molecular biology and medicine.
Related Diseases
Structural highlights
Overall Structure
This is a sample scene created with SAT to by Group, and another to make of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes.