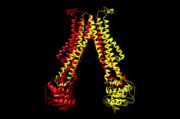
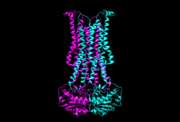
Flippases are the homodimeric transmembrane proteins located in the membrane. It helps phospholipid to transport from inner face to outer face of the cell membrane. It is composed with alpha-helix and beta sheets. The main three structural features of each monomer are an external helix, a belt of positively charged amino acids, and a binding site for an ATP molecule.
This is a default text for your page Sandbox flippases. Click above on edit this page to modify. Be careful with the < and > signs.
You may include any references to papers as in: the use of JSmol in Proteopedia [1] or to the article describing Jmol [2] to the rescue.
Function
Flippases flip the lipid from cytoplasmic side to periplasmic side.
Disease
Relevance
Structural highlights
This is a sample scene created with SAT to by Group, and another to make of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes.