Introduction
The human cystathionine β-synthase (hCBS) is natively a homotetrameric enzyme (EC 4.2.1.22) that catalyzes the condensation of homocysteine and serine into cystathionine (which is part of the cysteine biosynthesis pathway) as shown below [1]:
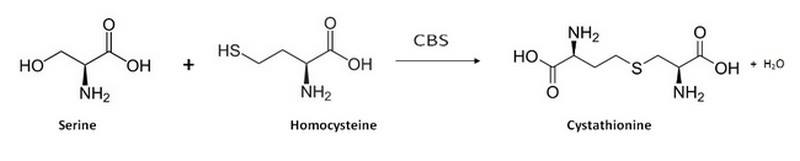 adpated from Wikipedia
adpated from Wikipedia
It is encoded by the CBS gene located on chromosome 21 (at position 22.3) [2].
Structure
A CBS monomer is a 551 amino-acids protein of 63 kDa. Each monomer binds two cofactors (the iron heme and the pyridoxal phosphate), as well as two substrates (homocysteine and serine) [1].
Hence, a CBS monomer contains (from N-terminal to C-terminal):
- a binding site located in a hydrophobic pocket (residues 50-67),
- a pyridoxal phosphate = (covalently linked to Lysine 119 amino group) situated in a (residues 70-382),
- a called Bateman module composed of two CBS domains (CBS1 and CBS2).
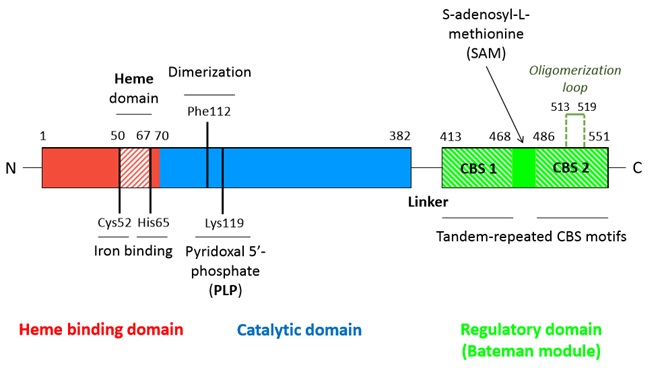 [1] [3] [4] [5]
[1] [3] [4] [5]
Cofactors
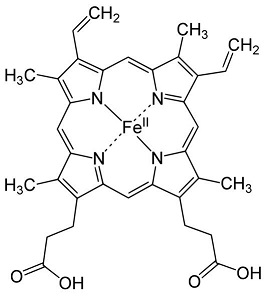 © Wikipedia
© Wikipedia
The heme is one of the two cofactors of hCBS.
It binds an hydrophobic pocket composed of the residues 50-67. The iron atom is hexacoordinated with the sulfhydryl group of Cys52 and the Nε2 atom of His65 (axial coordination) and with the four nitrogen atoms of the heme.
Although the heme is essential for activity in human CBS, its role still remains an enigma.
It is supposed to act as a redox sensor or as a way to facilitate a correct folding.
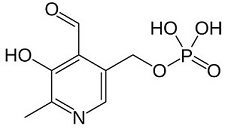 © Wikipedia
© Wikipedia
Pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) is the active form of the vitamin B6 (= pyridoxal, pyridoxamine and pyridoxine). It is the coenzyme of a lot of enzymatic reactions (transamination, decarboxylation, deamination, etc).
Action mechanism: the aldehyde group of PLP forms a Schiff-base linkage with the epsilon-amino group of an active site lysine residue on the enzyme. Then, the alpha-amino group of the substrate displaces the epsilon-amino group of the active-site lysine residue. Finally, the result is the formation of a new aldimine with the substrate, which is the intermediate for all reactions which are catalysed by PLP.
Enzymes which depend on PLP are mainly involved in the synthesis of amino acids and amino acid-derived metabolites. Moreover, they can also be found in the pathway of amino sugars and in the synthesis/catabolism of neurotransmitters.
An inadequate level of PLP in the brain can be responsible for neurological dysfunction, for example epilepsy.
Quaternary structure [4]
The hCBS is natively a homotetrameric enzyme. It has been suggested that two monomers form a dimer, and then two dimers form a tetramer.
Two monomers bind together to form a dimer through both hydrophobic and polar interactions within the catalytic core of each monomer. Hydrophobic interactions particularly involve two Phe112 (one from each monomer) which interact with each other. For hCBS there are no interactions between Bateman modules in a single dimer.
It involves the Bateman modules as well as the catalytic cores of each dimer. Each (loop 513-519) of a monomer of one dimer interacts with the catalytic core of a monomer of the other dimer. Those loops interact within a cavity (shaped by α-helix 5-6-12-15-16 and β-strands 5-6) of the catalytic core. The tetramer is an inactive form of the enzyme.
Allosteric regulation
Autoinhibition (at the dimer scale) [4] [8]
The Bateman modules natively prevent the access of the substrates to the catalytic site (PLP cavity) through:
- hydrophobic interactions between residues I537, L540, A544 of the CBS1 domain of the of one monomer with residues I166, V189, V206, L210, I214 of the of the other monomer,
- hydrogen bounds between residues T460, N463, S466, Y484 of the CBS2 domain of the of one monomer with residues E201, N194, R196, D198 of the of the of the other monomer.
These hydrophobic interactions, combined with the hydrogen bound network anchor the Bateman module of one monomer to the entrance of the catalytic core of the other monomer (close conformation), thus making it impossible for any substrate to get access to it.
Activation by S-adenosyl-L-methionine (SAM) [8]
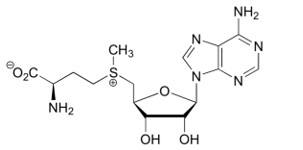 © Wikipedia
© Wikipedia
- SAM is the allosteric activator of the CBS. It binds in a region located between the CBS1 and CBS2 domains of the Bateman module which is solvent-exposed and has less hefty hydrophobic residues. In addition, this region forms a hydrophobic cage able to host the adenine ring. Moreover threonine (T535) and aspartate (D538) help stabilize the ribose through hydrogen bounds and polar interactions.
- Binding of SAM to the Bateman module destabilizes the interactions which sustain the tetramer structure and thus triggers the dissociation of the tetrameric structure into two dimers.
- SAM fixation on the C-terminal regulatory domain triggers the small rotation (or at least displacement) of the CBS1 and CBS2 of the Bateman module, thus distabilizing its interactions (hydrophobic interactions and hydrogen bounds) with the catalytic core of the other monomer. As a result, the Bateman module moves away from the catalytic core (this movement is facilitated since the linker region is long enough and made of flexible residues). , previously involved in maintaining the close conformation through their interaction with the Bateman module, then relax and therefore allow accessibility to the catalytic site (open conformation).
- SAM release leads to the return to the native inactive close conformation.
Disease
A tight control of cystathionine β-synthase level and activity is crucial for optimal cognitive function.
Due to the fact that the CBS gene is located on chromosome 21 (21q22.3), an overexpression of CBS is observed in patients with Down Syndrome, or trisomy 21.
Hence, Down Syndrome is characterized by high plasma levels of cystathionine and cysteine and this disorder is typically associated with mental retardation. [9]
On the contrary, a reduced activity of CBS leads to homocystinuria. This disorder is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern and is caused by loss-of-function mutations in the hCBS gene. Those mutations interfere with the activation of CBS.
Thus, Homocystinuria is characterized by high plasma levels of the toxic amino acid homocysteine and infants who develop this disease may have difficulties to grow and gain weight accompanied by mental retardation. [10]





