Function
Heat shock factor (HSF) are transcriptional activators of heat shock genes. HSF bind to heat shock sequence elements throughout the genome with a consensus array of three oppositely oriented sequence AGGAN and activate transcription. Each HSF monomer contains one C-terminal and 3 N-terminal leucine zippers. Two sequences flanking the N-terminal leucine zippers contain the consensus nuclear localization signal (NLS). The DNA-binding domain (DBD) of HSF lies in the N-terminal of the first NLS region[1].
Relevance
Depletion of HSF-1 is associated with accumulation of pathogenic androgen receptor in neurodegenerative diseases[2].
Structural highlights
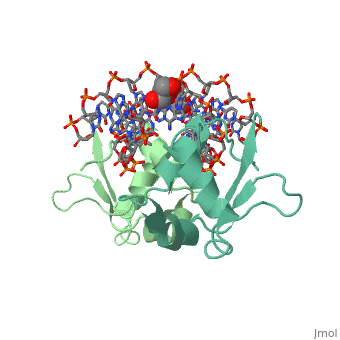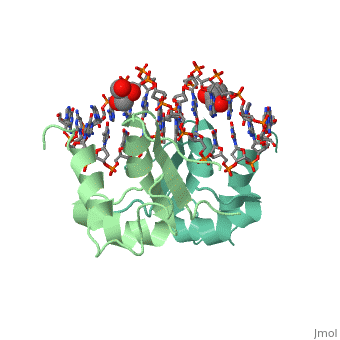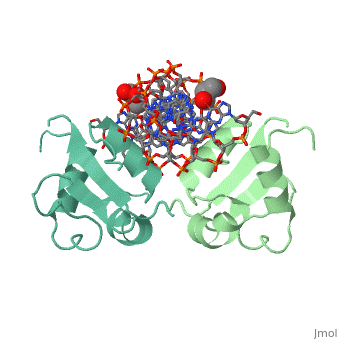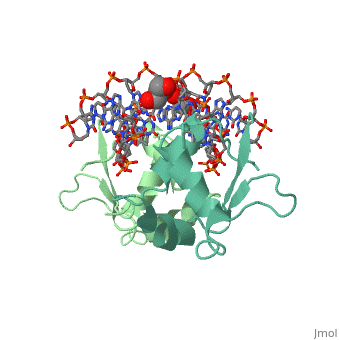
The DBD region of HSF shows multiple protein-DNA interactions as well as water-mediated interactions [3].
3D structures of heat shock factor
Updated on 20-March-2016
1hks, 1hkt – HSF DBD – Drosophila melanogaster – NMR
2ldu – HSF DBD – human - NMR
2hts, 1fbu – KlHSF DBD – Kluyveromyces lactis
3htf, 1fbq, 1fbs – KlHSF DBD (mutant)
3hts – KlHSF DBD + DNA
1fyk, 1fyl, 1fym – KlHSF DBD (mutant) + DNA
References
- ↑ Sarge KD, Murphy SP, Morimoto RI. Activation of heat shock gene transcription by heat shock factor 1 involves oligomerization, acquisition of DNA-binding activity, and nuclear localization and can occur in the absence of stress. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1392-407. PMID:8441385
- ↑ Kondo N, Katsuno M, Adachi H, Minamiyama M, Doi H, Matsumoto S, Miyazaki Y, Iida M, Tohnai G, Nakatsuji H, Ishigaki S, Fujioka Y, Watanabe H, Tanaka F, Nakai A, Sobue G. Heat shock factor-1 influences pathological lesion distribution of polyglutamine-induced neurodegeneration. Nat Commun. 2013;4:1405. doi: 10.1038/ncomms2417. PMID:23360996 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ncomms2417
- ↑ Littlefield O, Nelson HC. A new use for the 'wing' of the 'winged' helix-turn-helix motif in the HSF-DNA cocrystal. Nat Struct Biol. 1999 May;6(5):464-70. PMID:10331875 doi:10.1038/8269