From Proteopedia
proteopedia linkproteopedia link |
Function
Hyaluronidase (HU) hydrolyzes complex carbohydrates such as hyaluronan which is part of the extracellular matrix. The hydrolysis increases tissue permeability.
Relevance
HU is used in medicine to speed drug delivery. Hyaluronic acid (HUA) is a popular dermal filler material.
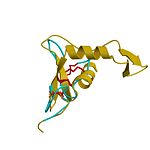 Superposition of the EGF-like domain of hyaluronidase-1 (yellow) and the heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor (light blue). The three disulfide bonds of the EGF domains (highlighted red) exhibit the same pattern in the primary structure and are located in similar positions in the 3D structure. | 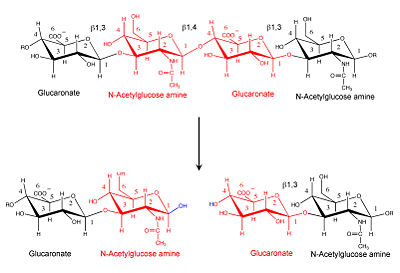 Hyaluronidase cleaves the β1,4-glycosidic bond of the glycosaminoglycan hyaluronan |
|
3D structures of hyaluronidase
Updated on 27-March-2016
Reference
Structure of human hyaluronidase-1, a hyaluronan hydrolyzing enzyme involved in tumor growth and angiogenesis., Chao KL, Muthukumar L, Herzberg O, Biochemistry. 2007 Jun 12;46(23):6911-20. Epub 2007 May 16. PMID:17503783
Created with the participation of Osnat Herzberg, Eran Hodis, Joel L. Sussman, Jaime Prilusky.


