Function
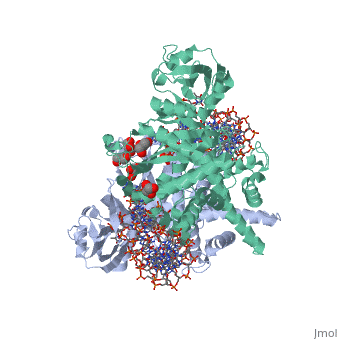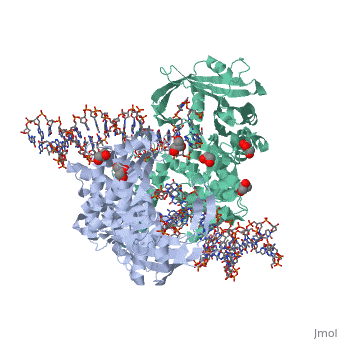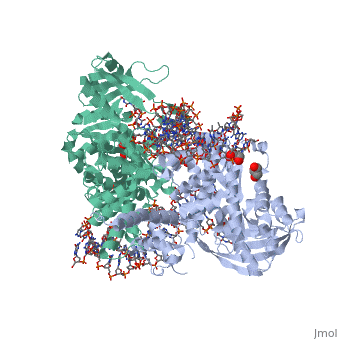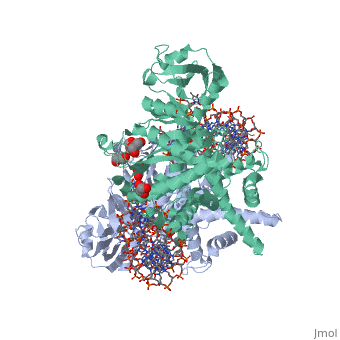
Transposases bind to the ends of a transposon and catalyze its movement to another part of the genome by a cut-and-paste mechanism[1].
- Mu transposase (MuA) is essential for integration, replication-transposition and excision of bacteriophage Mu DNA into multiple sites of bacterial genome. Mu transposition occurs within the transposome which is a protein-DNA complex which includes 4 subunits of MuA[2].
- Hermes transposase is a fly protein[3].
- Dra2 transposase is a Deinococcus radiodurans protein
- Tn5 transposase active site contains the DDE motif which catalyzes the movement of the transposon[4].
- Mos1 transposase mediates the movement of Mos1 transposon[5]
- Tc3 transposase mediates the movement of Tc3 transposon in C. elegans[6]
Structural highlights
Transposase contains a DDE motif in its active site[7] enabling it to coordinate the binding of divalent metal ions. The metal ions affect transposase reactivity.