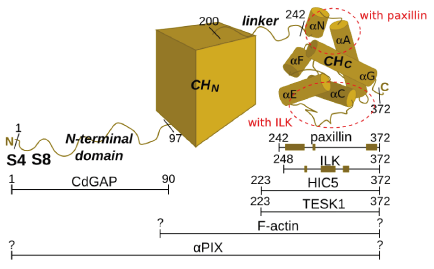
Parvin
From Proteopedia
| |||||||||||
3D structures of Alpha-parvin
Updated on 02-November-2016
3kmu - hAPAR + integrin-linked kinase pseudokinase domain – human
3rep, 3kmw – hAPAR + integrin-linked kinase pseudokinase domain + ATP
2vzc – hAPAR calponin homology domain
2vzd, 2vzg, 2vzi - hAPAR calponin homology domain + paxillin motif
2k2r - hAPAR calponin homology domain + paxillin LD1 motif - NMR
References
- ↑ Olski TM, Noegel AA, Korenbaum E. Parvin, a 42 kDa focal adhesion protein, related to the alpha-actinin superfamily. J Cell Sci. 2001 Feb;114(Pt 3):525-38. PMID:11171322
- ↑ Nikolopoulos SN, Turner CE. Actopaxin, a new focal adhesion protein that binds paxillin LD motifs and actin and regulates cell adhesion. J Cell Biol. 2000 Dec 25;151(7):1435-48. PMID:11134073
- ↑ Tu Y, Huang Y, Zhang Y, Hua Y, Wu C. A new focal adhesion protein that interacts with integrin-linked kinase and regulates cell adhesion and spreading. J Cell Biol. 2001 Apr 30;153(3):585-98. PMID:11331308
- ↑ Montanez E, Wickstrom SA, Altstatter J, Chu H, Fassler R. Alpha-parvin controls vascular mural cell recruitment to vessel wall by regulating RhoA/ROCK signalling. EMBO J. 2009 Oct 21;28(20):3132-44. Epub 2009 Oct 1. PMID:19798050 doi:10.1038/emboj.2009.295
- ↑ Clarke DM, Brown MC, LaLonde DP, Turner CE. Phosphorylation of actopaxin regulates cell spreading and migration. J Cell Biol. 2004 Sep 13;166(6):901-12. Epub 2004 Sep 7. PMID:15353548 doi:10.1083/jcb.200404024
- ↑ LaLonde DP, Brown MC, Bouverat BP, Turner CE. Actopaxin interacts with TESK1 to regulate cell spreading on fibronectin. J Biol Chem. 2005 Jun 3;280(22):21680-8. Epub 2005 Apr 6. PMID:15817463 doi:10.1074/jbc.M500752200
- ↑ LaLonde DP, Grubinger M, Lamarche-Vane N, Turner CE. CdGAP associates with actopaxin to regulate integrin-dependent changes in cell morphology and motility. Curr Biol. 2006 Jul 25;16(14):1375-85. PMID:16860736 doi:S0960-9822(06)01676-9
- ↑ Yang Y, Guo L, Blattner SM, Mundel P, Kretzler M, Wu C. Formation and phosphorylation of the PINCH-1-integrin linked kinase-alpha-parvin complex are important for regulation of renal glomerular podocyte adhesion, architecture, and survival. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005 Jul;16(7):1966-76. Epub 2005 May 4. PMID:15872073 doi:10.1681/ASN.2004121112
- ↑ Hynes RO. The extracellular matrix: not just pretty fibrils. Science. 2009 Nov 27;326(5957):1216-9. PMID:19965464 doi:10.1126/science.1176009
- ↑ Barczyk M, Carracedo S, Gullberg D. Integrins. Cell Tissue Res. 2010 Jan;339(1):269-80. Epub 2009 Aug 20. PMID:19693543 doi:10.1007/s00441-009-0834-6
- ↑ Wolfenson H, Henis YI, Geiger B, Bershadsky AD. The heel and toe of the cell's foot: a multifaceted approach for understanding the structure and dynamics of focal adhesions. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2009 Nov;66(11):1017-29. PMID:19598236 doi:10.1002/cm.20410
- ↑ Zaidel-Bar R, Itzkovitz S, Ma'ayan A, Iyengar R, Geiger B. Functional atlas of the integrin adhesome. Nat Cell Biol. 2007 Aug;9(8):858-67. PMID:17671451 doi:10.1038/ncb0807-858
- ↑ Wolfenson H, Henis YI, Geiger B, Bershadsky AD. The heel and toe of the cell's foot: a multifaceted approach for understanding the structure and dynamics of focal adhesions. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2009 Nov;66(11):1017-29. PMID:19598236 doi:10.1002/cm.20410
- ↑ Zaidel-Bar R, Geiger B. The switchable integrin adhesome. J Cell Sci. 2010 May 1;123(Pt 9):1385-8. PMID:20410370 doi:10.1242/jcs.066183
- ↑ Gardel ML, Schneider IC, Aratyn-Schaus Y, Waterman CM. Mechanical integration of actin and adhesion dynamics in cell migration. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2010 Nov 10;26:315-33. PMID:19575647 doi:10.1146/annurev.cellbio.011209.122036
- ↑ Attwell S, Mills J, Troussard A, Wu C, Dedhar S. Integration of cell attachment, cytoskeletal localization, and signaling by integrin-linked kinase (ILK), CH-ILKBP, and the tumor suppressor PTEN. Mol Biol Cell. 2003 Dec;14(12):4813-25. Epub 2003 Sep 5. PMID:12960424 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E03-05-0308
- ↑ Olski TM, Noegel AA, Korenbaum E. Parvin, a 42 kDa focal adhesion protein, related to the alpha-actinin superfamily. J Cell Sci. 2001 Feb;114(Pt 3):525-38. PMID:11171322
- ↑ Wang X, Fukuda K, Byeon IJ, Velyvis A, Wu C, Gronenborn A, Qin J. The structure of alpha-parvin CH2-paxillin LD1 complex reveals a novel modular recognition for focal adhesion assembly. J Biol Chem. 2008 Jul 25;283(30):21113-9. Epub 2008 May 28. PMID:18508764 doi:10.1074/jbc.M801270200
- ↑ Lorenz S, Vakonakis I, Lowe ED, Campbell ID, Noble ME, Hoellerer MK. Structural analysis of the interactions between paxillin LD motifs and alpha-parvin. Structure. 2008 Oct 8;16(10):1521-31. PMID:18940607 doi:10.1016/j.str.2008.08.007
- ↑ Nikolopoulos SN, Turner CE. Actopaxin, a new focal adhesion protein that binds paxillin LD motifs and actin and regulates cell adhesion. J Cell Biol. 2000 Dec 25;151(7):1435-48. PMID:11134073
- ↑ Lorenz S, Vakonakis I, Lowe ED, Campbell ID, Noble ME, Hoellerer MK. Structural analysis of the interactions between paxillin LD motifs and alpha-parvin. Structure. 2008 Oct 8;16(10):1521-31. PMID:18940607 doi:10.1016/j.str.2008.08.007
- ↑ LaLonde DP, Brown MC, Bouverat BP, Turner CE. Actopaxin interacts with TESK1 to regulate cell spreading on fibronectin. J Biol Chem. 2005 Jun 3;280(22):21680-8. Epub 2005 Apr 6. PMID:15817463 doi:10.1074/jbc.M500752200
- ↑ LaLonde DP, Grubinger M, Lamarche-Vane N, Turner CE. CdGAP associates with actopaxin to regulate integrin-dependent changes in cell morphology and motility. Curr Biol. 2006 Jul 25;16(14):1375-85. PMID:16860736 doi:S0960-9822(06)01676-9
- ↑ LaLonde DP, Grubinger M, Lamarche-Vane N, Turner CE. CdGAP associates with actopaxin to regulate integrin-dependent changes in cell morphology and motility. Curr Biol. 2006 Jul 25;16(14):1375-85. PMID:16860736 doi:S0960-9822(06)01676-9
- ↑ Curtis M, Nikolopoulos SN, Turner CE. Actopaxin is phosphorylated during mitosis and is a substrate for cyclin B1/cdc2 kinase. Biochem J. 2002 Apr 15;363(Pt 2):233-42. PMID:11931650
- ↑ Clarke DM, Brown MC, LaLonde DP, Turner CE. Phosphorylation of actopaxin regulates cell spreading and migration. J Cell Biol. 2004 Sep 13;166(6):901-12. Epub 2004 Sep 7. PMID:15353548 doi:10.1083/jcb.200404024
- ↑ Ishibe S, Joly D, Zhu X, Cantley LG. Phosphorylation-dependent paxillin-ERK association mediates hepatocyte growth factor-stimulated epithelial morphogenesis. Mol Cell. 2003 Nov;12(5):1275-85. PMID:14636584
- ↑ Attwell S, Mills J, Troussard A, Wu C, Dedhar S. Integration of cell attachment, cytoskeletal localization, and signaling by integrin-linked kinase (ILK), CH-ILKBP, and the tumor suppressor PTEN. Mol Biol Cell. 2003 Dec;14(12):4813-25. Epub 2003 Sep 5. PMID:12960424 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E03-05-0308
- ↑ Clarke DM, Brown MC, LaLonde DP, Turner CE. Phosphorylation of actopaxin regulates cell spreading and migration. J Cell Biol. 2004 Sep 13;166(6):901-12. Epub 2004 Sep 7. PMID:15353548 doi:10.1083/jcb.200404024
- ↑ Montanez E, Wickstrom SA, Altstatter J, Chu H, Fassler R. Alpha-parvin controls vascular mural cell recruitment to vessel wall by regulating RhoA/ROCK signalling. EMBO J. 2009 Oct 21;28(20):3132-44. Epub 2009 Oct 1. PMID:19798050 doi:10.1038/emboj.2009.295
- ↑ LaLonde DP, Brown MC, Bouverat BP, Turner CE. Actopaxin interacts with TESK1 to regulate cell spreading on fibronectin. J Biol Chem. 2005 Jun 3;280(22):21680-8. Epub 2005 Apr 6. PMID:15817463 doi:10.1074/jbc.M500752200
- ↑ LaLonde DP, Grubinger M, Lamarche-Vane N, Turner CE. CdGAP associates with actopaxin to regulate integrin-dependent changes in cell morphology and motility. Curr Biol. 2006 Jul 25;16(14):1375-85. PMID:16860736 doi:S0960-9822(06)01676-9
- ↑ Yang Y, Guo L, Blattner SM, Mundel P, Kretzler M, Wu C. Formation and phosphorylation of the PINCH-1-integrin linked kinase-alpha-parvin complex are important for regulation of renal glomerular podocyte adhesion, architecture, and survival. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005 Jul;16(7):1966-76. Epub 2005 May 4. PMID:15872073 doi:10.1681/ASN.2004121112
- ↑ Attwell S, Mills J, Troussard A, Wu C, Dedhar S. Integration of cell attachment, cytoskeletal localization, and signaling by integrin-linked kinase (ILK), CH-ILKBP, and the tumor suppressor PTEN. Mol Biol Cell. 2003 Dec;14(12):4813-25. Epub 2003 Sep 5. PMID:12960424 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E03-05-0308
- ↑ Schultz J, Milpetz F, Bork P, Ponting CP. SMART, a simple modular architecture research tool: identification of signaling domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 May 26;95(11):5857-64. PMID:9600884
- ↑ Lorenz S, Vakonakis I, Lowe ED, Campbell ID, Noble ME, Hoellerer MK. Structural analysis of the interactions between paxillin LD motifs and alpha-parvin. Structure. 2008 Oct 8;16(10):1521-31. PMID:18940607 doi:10.1016/j.str.2008.08.007
- ↑ Espinoza-Fonseca LM. Reconciling binding mechanisms of intrinsically disordered proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009 May 8;382(3):479-82. Epub 2009 Mar 3. PMID:19265676 doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.02.151
- ↑ Iakoucheva LM, Radivojac P, Brown CJ, O'Connor TR, Sikes JG, Obradovic Z, Dunker AK. The importance of intrinsic disorder for protein phosphorylation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004 Feb 11;32(3):1037-49. Print 2004. PMID:14960716 doi:10.1093/nar/gkh253
- ↑ Collins MO, Yu L, Campuzano I, Grant SG, Choudhary JS. Phosphoproteomic analysis of the mouse brain cytosol reveals a predominance of protein phosphorylation in regions of intrinsic sequence disorder. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2008 Jul;7(7):1331-48. Epub 2008 Apr 3. PMID:18388127 doi:10.1074/mcp.M700564-MCP200
- ↑ Friedberg F. Singlet CH domain containing human multidomain proteins: an inventory. Mol Biol Rep. 2010 Mar;37(3):1531-9. Epub 2009 May 21. PMID:19459066 doi:10.1007/s11033-009-9554-y
- ↑ Friedberg F. Duplex (or quadruplet) CH domain containing human multidomain proteins: an inventory. Mol Biol Rep. 2010 Apr;37(4):1707-16. Epub 2009 Jun 30. PMID:19565353 doi:10.1007/s11033-009-9589-0
- ↑ Stradal T, Kranewitter W, Winder SJ, Gimona M. CH domains revisited. FEBS Lett. 1998 Jul 17;431(2):134-7. PMID:9708889
- ↑ Sjoblom B, Ylanne J, Djinovic-Carugo K. Novel structural insights into F-actin-binding and novel functions of calponin homology domains. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2008 Dec;18(6):702-8. Epub 2008 Nov 13. PMID:18952167 doi:10.1016/j.sbi.2008.10.003
- ↑ Gimona M, Djinovic-Carugo K, Kranewitter WJ, Winder SJ. Functional plasticity of CH domains. FEBS Lett. 2002 Feb 20;513(1):98-106. PMID:11911887
- ↑ Lorenz S, Vakonakis I, Lowe ED, Campbell ID, Noble ME, Hoellerer MK. Structural analysis of the interactions between paxillin LD motifs and alpha-parvin. Structure. 2008 Oct 8;16(10):1521-31. PMID:18940607 doi:10.1016/j.str.2008.08.007
- ↑ Lorenz S, Vakonakis I, Lowe ED, Campbell ID, Noble ME, Hoellerer MK. Structural analysis of the interactions between paxillin LD motifs and alpha-parvin. Structure. 2008 Oct 8;16(10):1521-31. PMID:18940607 doi:10.1016/j.str.2008.08.007
- ↑ Wang X, Fukuda K, Byeon IJ, Velyvis A, Wu C, Gronenborn A, Qin J. The structure of alpha-parvin CH2-paxillin LD1 complex reveals a novel modular recognition for focal adhesion assembly. J Biol Chem. 2008 Jul 25;283(30):21113-9. Epub 2008 May 28. PMID:18508764 doi:10.1074/jbc.M801270200
- ↑ Fukuda K, Gupta S, Chen K, Wu C, Qin J. The pseudoactive site of ILK is essential for its binding to alpha-Parvin and localization to focal adhesions. Mol Cell. 2009 Dec 11;36(5):819-30. PMID:20005845 doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2009.11.028
- ↑ Lorenz S, Vakonakis I, Lowe ED, Campbell ID, Noble ME, Hoellerer MK. Structural analysis of the interactions between paxillin LD motifs and alpha-parvin. Structure. 2008 Oct 8;16(10):1521-31. PMID:18940607 doi:10.1016/j.str.2008.08.007
- ↑ Lorenz S, Vakonakis I, Lowe ED, Campbell ID, Noble ME, Hoellerer MK. Structural analysis of the interactions between paxillin LD motifs and alpha-parvin. Structure. 2008 Oct 8;16(10):1521-31. PMID:18940607 doi:10.1016/j.str.2008.08.007
- ↑ Lorenz S, Vakonakis I, Lowe ED, Campbell ID, Noble ME, Hoellerer MK. Structural analysis of the interactions between paxillin LD motifs and alpha-parvin. Structure. 2008 Oct 8;16(10):1521-31. PMID:18940607 doi:10.1016/j.str.2008.08.007
- ↑ Lorenz S, Vakonakis I, Lowe ED, Campbell ID, Noble ME, Hoellerer MK. Structural analysis of the interactions between paxillin LD motifs and alpha-parvin. Structure. 2008 Oct 8;16(10):1521-31. PMID:18940607 doi:10.1016/j.str.2008.08.007
- ↑ Fukuda K, Gupta S, Chen K, Wu C, Qin J. The pseudoactive site of ILK is essential for its binding to alpha-Parvin and localization to focal adhesions. Mol Cell. 2009 Dec 11;36(5):819-30. PMID:20005845 doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2009.11.028
- ↑ Fukuda K, Gupta S, Chen K, Wu C, Qin J. The pseudoactive site of ILK is essential for its binding to alpha-Parvin and localization to focal adhesions. Mol Cell. 2009 Dec 11;36(5):819-30. PMID:20005845 doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2009.11.028
- ↑ Wickstrom SA, Lange A, Montanez E, Fassler R. The ILK/PINCH/parvin complex: the kinase is dead, long live the pseudokinase! EMBO J. 2010 Jan 20;29(2):281-91. Epub 2009 Dec 24. PMID:20033063 doi:10.1038/emboj.2009.376
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Marcin Jozef Suskiewicz, Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, David Canner, Jaime Prilusky