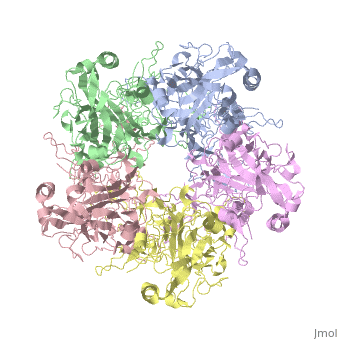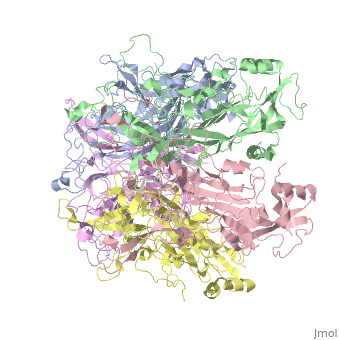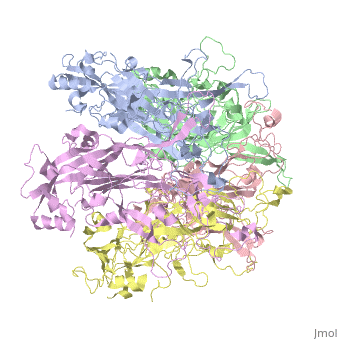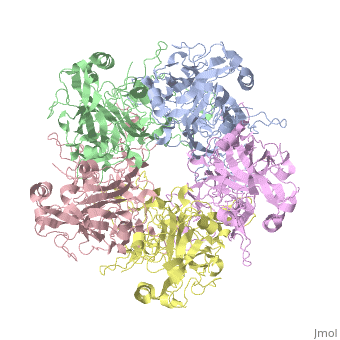Introduction
Gardasil 9 is a recombinant vaccine for the human papillomavirus and protects from the 9 most common forms that are known to cause the majority of HPV-related diseases and cancer. These types are 6, 11, 16, 18, 31, 33, 45, 52, and 58. HPVs are the causative agents of human neoplasia such as warts and cancers [1]. The HPV vaccine is recommended for children ages 11 to 12 and is intended for females ages 9-25 and protects against cervical cancer, vulvar and vaginal cancer, anal cancer, and genital warts. The vaccine is also intended for males ages 9-26 and protects against anal cancer and genital warts [2]. Gardasil vaccine is made up of proteins that resemble the ones on the outside of an actual human papillomavirust [3].The main ingredient in Gardasil 9 is the [4].
Function
Gardasil mimics the , but it does not contain any viral DNA which removes any chance of infection of the HPV virus. This vaccine allows the body to create antibodies to HPV in order to be able to remove the virus if it is introduced in the body. Since the L1 protein is the main structural component of HPV and Gardasil, Gardasil can use this protein to remove HPV from the infected cells [3]. The antibodies provided by Gardasil prevent HPV infection by keeping the virus from entering the epithelial cells of the genitals. However, the antibodies created do not last forever, so the gardasil vaccine will need to be followed up with booster shots[5].
Structural Highlights
The main ingredient in Gardasil 9 is L1 Major Capsid Protein [4]. L1 Major Capsid Protein has 72 pentamers that are linked together by ,shown in red, that creates an icosahedral capsid with a T=7 symmetry, which is a spherical protein [6]. L1 Major Capsid Protein is associated with L2 Minor Capsid Protein. The L1 Major Capsid Protein is built of mainly [7] shown in orange.
Relevance to Human Health and Disease