Elizeu/sandbox/citocromo c
From Proteopedia
User: Julie Langlois/Sandbox NCBI Accession: P42363.1 Uniprot Accesion: POA4G2 PDB ID: 3ZK7 Molecular weight: 34,538 kDa
Contents |
Overview
PsaA protein
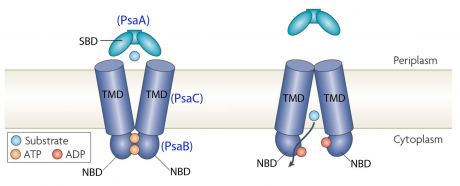
PsaA (Pneumococcal surface antigen A) is a multi-functional lipoprotein detected on all known serotypes of Streptococcus pneumoniae. This lipoprotein belongs to the ABC-type transport protein complex that transports Mn2+. ABC means ATP binding complex. PsaA is also an adhesion factor that plays a major role in pneumococcal attachment to the host cell and virulence. PsaA is hidden beneath the cell wall. PsaA protein is involved in in colonization of the nasopharyngeal mucosal.
This transporter is composed of the products of three genes, psaB (ATP-binding protein), psaC (integral membrane protein), and psaA (solute-binding lipoprotein), which are organized in an operon with a gene encoding PsaD, a thiol peroxidase.
Zinc in excess has significant toxicity to bacteria because it is an important innate defence mechanism. There are many Zinc in human body. Manganese is important for the virulence, growth and proliferation of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Zinc could compete for Manganese binding. However Manganese has more affinity for PsaA than Zinc but Zinc is not transported by the ABC-transporter. Zinc competition reduces intracellular Manganse resulting in up-regulation of PsaBCA expression.
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Streptococcus pneumoniae is a Gram positive cocci (with a diameter from 0.5 to 1 μm) and a member of the genus Streptococcus. It can live under aerobic or anaerobic conditions. It resides in the nasopharynx of healthy carriers. However the bacterium may become pathogenic in elderly and immunocompromised people and children. Then it can spread to other locations and cause disease. Its genome of S. pneumoniae is a closed, circular DNA structure that contains between 2.0 and 2.1 million base pairs.
Structure
|
|
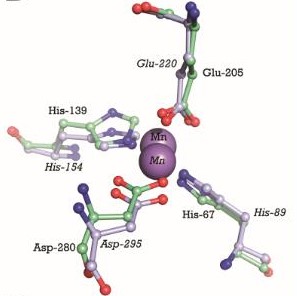 This image shows the metal binding site in more detail, with the MntC residues and Manganese. Manganse ions are shown as purple spheres. We can see that Manganese interacts with Histine residues, Aspartique acid residues and Glutamique acid residues.
This image shows the metal binding site in more detail, with the MntC residues and Manganese. Manganse ions are shown as purple spheres. We can see that Manganese interacts with Histine residues, Aspartique acid residues and Glutamique acid residues.
This is a test to add a in the Sandbox
Protein-protein interaction
Function
Disease
Meningitis
Otitis
Pneumonia
PsaA protein is an adhesin which is involved in colonization of the nasopharyngeal mucosal. Moreover, alveolar pneumonia is caused by the spread of Streptococcus pneumoniae from nasopharynx. Therefore PsaA protein is involved in infection of pulmonary parenchyma by Streptococcus pneumoniae. Sometimes, Streptococcus pneumoniae pass into the blood and causes a bacteremia besides pneumonia.
Application in Biotechnology
PsaA is being actively evaluated as a component of a vaccin in formulations composed of pneumococcal common proteins. PsaA has been expressed as an E.coli recombinant protein, purified, and evaluated in a phase one clinical trial.
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Julie Langlois, Atena Farhangian, Rebecca Holstein, Elizabeth A. Dunlap, Katherine Reynolds, Elizeu Santos, Noam Gonen, Anna Lohning, Idan Ben-Nachum, Brian Ochoa, Shai Biran, Gauri Misra, Shira Weingarten-Gabbay, Keni Vidilaseris, Jamie Costa, Abhinav Mittal, Urs Leisinger, Madison Walberry, Edmond R Atalla, Brett M. Thumm, Brooke Fenn, Joel L. Sussman, Mati Cohen, Vesta Nwankwo, Dotan Shaniv, Gulalai Shah