Fructose Bisphosphate Aldolase
Introduction and Structure
Fructose bisphosphate aldolase is an enzyme in glycolysis and gluconeogenesis. Glycolyis is responsible for the conversion of glucose into two three-carbon pyruvate molecules without the need for oxygen. The process generates two net ATP. The overall reaction is:
Glucose + 2 NAD+ + 2 ADP + 2 Pi --> 2 pyruvate (3-carbon product) + 2 NADH + 2 ATP + 2 H20 + 4 H+
Gluconeogenesis is responsible for maintaining the appropriate levels of blood glucose in animals by generating glucose from non-carbohydrate precursors. Gluconeogenesis can make glucose from lactate, pyruvate, citric acid cycle intermediates and from most amino acids (the exceptions being leucine and lysine). The common intermediate for all of the precursors on their way to becoming glucose must be oxaloacetate.
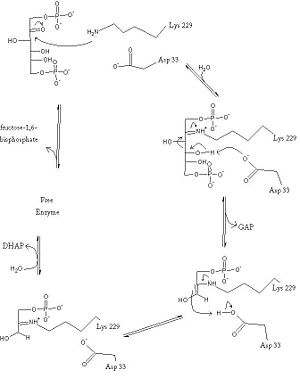
The aldolase catalyzes the reversible cleavage of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate into dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (GAP). Different isozymes of aldolase can also catalyze the cleavage of fructose 1-phosphate to diydroxyacetone and glyceraldehyde (GA). Different isozymes exhibit preferences for either or both of the substrates, depending on the role of the aldolase (i.e. gluconeogenesis versus glycolysis).[1] See also Enzimas: complejo enzima-sustrato (in Spanish) and Glycolysis Enzymes.
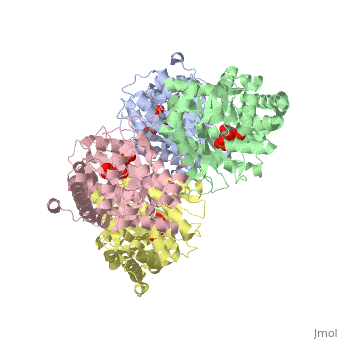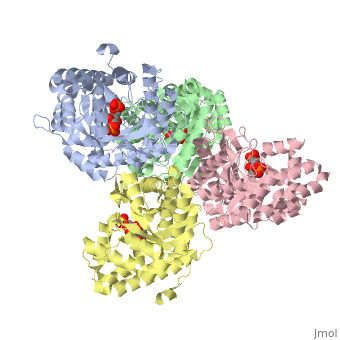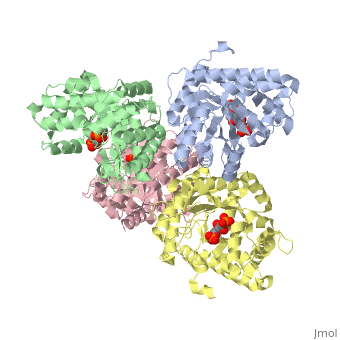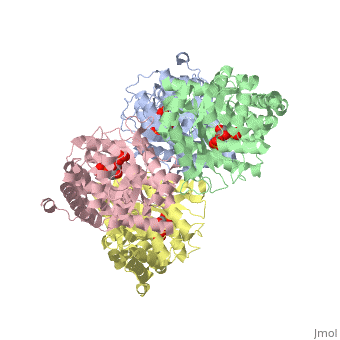
While it can exist as a monomer, it normally exists as a . The enzyme is an a/B protein with a TIM beta/alpha beta fold. The fold designation is based upon the nine alpha helices and eight parallel beta sheets in a closed barrel of each monomeric subunit. It is part of the aldolase superfamily and the class I aldolases.[2] can be seen in their specific regions mostly concentric to the active site, represented by the blue and red residues.
Although some form of fructose bisphosphate aldolase is present in nearly all living things, certain isoforms carry a large degree of conservation. The enzyme from rabbit muscle has nearly the tertiary and primary structure as the enzyme in human muscle. As a result, implications from rabbit muscle aldolase also reveal a great deal about the human forms of the enzyme. [3]
Binding and Catalysis
As an enzyme, the aldolase must not only encourage and favor the hydrolysis of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate, but also bind the substrate so as to hold it in the active site. The main-chain nitrogens of Ser271 and Gly272 hold the 1-phosphate group while the Lys41, Arg42 and Arg303 residues hold the 6-phosphate group. The five proposed binding residues are in close proximity to the catalytic Lys229, implicating them as participants in the binding process.[4] The , which sits just outside of the barrel and catalytic site, of the enzyme also appears to contribute to the catalytic process of the aldolase. Mutations or suppression of the final tyrosine residue (Tyr363) causes a notable drop in the activity of the enzyme. Two cysteine residues have also been implicated in the catalytic process. Though they do not appear to be necessary for catalysis, modification of them does result in a decrease in catalytic activity. The two Cys residues are far from the active site, but do impact the movement of the C-terminus of the enzyme, which further implicates the terminus as participatory in the catalysis.
The reaction is an aldol cleavage, or otherwise termed, retro aldo condensation. Catalysis occurs first when the nucleophilic ε-amine group of Lys229 attacks the carbonyl carbon of the substrate (FBP) in its open-ring state, pushing an electron pair to the oxygen of the carbonyl. The oxygen is protonated and leaves as water as a protonated is produced (an imine resulting from a ketone and amine) with the open-ring form of FBP, accompanied by electrostatic stabilization from Aldol cleavage between C3 and C4 produces GAP and an enamine precursor to DHAP.[1] The cleavage is facilitated by the positive charge from the Schiff base. The subsequent electron movement, which alleviates the positive charge, also breaks the C3-C4 bond.[3] Tautomerization, protonation and the hydrolysis of the Schiff base produce the final product of DHAP and regenerate the enzyme. The catalysis is driven by the more favorable stability of the protonated Schiff base compared to the enolate that would appear in basic catalysis pathways.[1]
Kinetics
Isotopic labelling has revealed the rate-determining step for the reaction. Either the carbon-carbon bond cleavage or the release of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate comprise the slow step of the catalysis reaction; however, studies do indicate that the GAP release is likely the slowest step.[3]
It has been shown that aldolase is inhibited allosterically by oxidized glutathione, which is an oxidizing species biologically present. The glutathione oxidizes a thiol 25 angstroms from the catalytic site, which subsequently causes a drop in catalytic activity. In addition, the enzyme shows no positive cooperativity, despite being an oligomer. In fact, kinetics data actually show that the enzyme exhibits negative cooperativity. Thus the catalysis is highly compartmentalized within each subunit and binding causes little distal change of the enzymes structure.[5]
Regulation
The regulation of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate aldolase is not well understood, but the understanding is every-increasing. As it is currently observed, aldolase C appears to be regulated mainly by the gene expression--the concentration of mRNA in the cytoplasm.[6] It is also known that adenosine 3',5'-cyclicmonophosphate (cAMP) affects the expression of the gene. cAMP concentration has been positively correlated with aldolase C expression. It is believed that cAMP acts upon a section of the promotor region, distal element D, causing the transcriptional promoter, NGFI-B, to bind. Once bound, the promoter activates the transcription of the gene coding for fructose bisphosphate aldolase.[7] Given the inhibitory effects of an oxidant in the presence of aldolase, it is possible that this could be a mechanism of regulation of the enzyme. The deactivation that accompanies the oxidation of the surface thiol of Cys72 could be used intracellularly to slow the catalysis of the enzyme and regulate glycolysis.[5]