This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Sandbox Reserved 1071
From Proteopedia
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 02/09/2015, through 05/31/2016 for use in the course "CH462: Biochemistry 2" taught by Geoffrey C. Hoops at the Butler University. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1051 through Sandbox Reserved 1080. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Contents |
DgcZ from E. coli
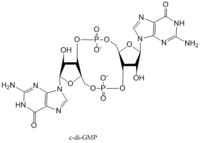
Diguanylate cyclases synthesize cyclic dimeric-GMP (c-di-GMP) from two GTP molecules. C-di-GMP is a second messenger in the production of poly-β-1,6-N-acetylglucosamine (poly-GlcNAc) , a polysaccharide required for E. coli biofilm production. This biofilm allows E. coli to adhere to extracellular surfaces. The DgcZ protein is made of two domains: the catalytic GGDEF domain responsible for sythnesizing c-di-GMP and the regulatory CZB domain that binds zinc. When zinc is bound, the CZB and GGDEF domains adopt conformations that inhibit DgcZ function. DgcZ binds zinc with sub-femtomolar affinity, making it very likely that zinc will bind in the CZB domain.
| |||||||||||
Structure
Catalytic GGDEF Domain
E. coli DgcZ is a protein made of two domains each of which is a symmetric homodimer. The GGDEF domain is made of a central five-stranded β-sheet with five α-helices surrounding it. Each dimer contains an active half-site that, when combined together in a productive conformation, form the entire active site. Each half-site binds one GTP. The guanyl base forms hydrogen bonds with asparagine-173 and aspartate-182 to hold it in the active site. A magnesium2+ ion stabilizes the negative charges on the phosphate groups. When in the productive conformation, each GTP is held in close proximity with the α-phosphate groups overlapping C3 of the ribose. This conformation allows the α-phospate of one GTP to react with alcohol on C3 on the ribose of the other GTP, resulting in a cyclization of the two molecules into cyclic-dimeric-GMP.