Eag domain-CNBHD complex of the mouse EAG1
From Proteopedia
Introduction:
The KCNH voltage-gated channels are transmembrane channels highly selective for potassium and sensitive to voltage changes in the cells’ membrane potential.They play a crucial roles in repolarization of cells to their resting state and in various diseases such as cardiac long QT syndrome type 2 (LQT2)[1], epilepsy[2], schizophrenia[3] and cancer[4]. The KCNH channels family has unique intracellular domains that distinguish them from other voltage-gated channels. The amino terminal contains an eag domain and the C-terminus contains a cyclic nucleotide binding homology domain (CNBDH).
Intracellular domain structure of KCNH1 (mEAG):
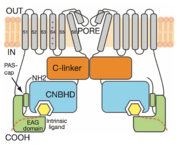
KCNH channels have two intracellular domains that provide the unique properties of regulation and gating to this channel family. The CNBHD (residues 517-698) located on the C-terminus, however dose not bind cyclic nucleotides and regulates gating in unknown mechanism. The eag domain (residues 1-136) composed of a PAS domain (110 amino acid) and highly conserved PAS-cap (25 amino acid)[5]. The eag domain regulates the activation and inactivation in unknown mechanism[6]. The interface between the eag domain and the CNBHD is with an average buried solvent-accessible surface area of ~ (1,400 A ̊2). The interface consists of three sub-regions: (1) the intrinsic ligand motif of the CNBHD interacts with the aB-helix in the PAS domain; (2) the bA and bB strands of the PAS domain interact with the post-CNBHD segment of the CNBHD; and (3) an amphipathic helix (aCAP) in the PAS-cap domain forms an inter- action with the b-roll of the CNBHD[7].
- ↑ Sanguinetti, M. C. & Tristani-Firouzi, M. hERG potassium channels and cardiac arrhythmia. Nature 440, 463–469 (2006).
- ↑ Zhang, X. et al. Deletion of the potassium channel Kv12.2 causes hippocampal hyperexcitability and epilepsy. Nature Neurosci. 13, 1056–1058 (2010).
- ↑ Huffaker, S. J. et al. A primate-specific, brain isoform of KCNH2 affects cortical physiology, cognition, neuronal repolarization and risk of schizophrenia. Nature Med. 15, 509–518 (2009).
- ↑ Camacho, J. Ether a` go-go potassium channels and cancer. Cancer Lett. 233, 1–9 (2006).
- ↑ Morais Cabral, J. H. et al. Crystal structure and functional analysis of the HERG potassium channel N terminus: a eukaryotic PAS domain. Cell 95, 649–655 (1998)
- ↑ Gustina, A. S. & Trudeau, M. C. HERG potassium channel regulation by the N-terminal eag domain. Cell. Signal. 24, 1592–1598 (2012)
- ↑ Haitin, Y., A.E. Carlson, and W.N. Zagotta. 2013. The structural mechanism of KCNH-channel regulation by the eag domain. Nature