User:Khadar Abdi/Sandbox1
From Proteopedia
Threonyl-tRNA Synthetase/ligase
Function/MechanismThreonyl t-RNA Synthetase or Threonyl-tRNA ligase or TARS is class II Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase enzymes. These enzymes primary function are to added the respective amino acid to the respective transfer Ribonucleic Acid (tRNA-AA) The main function of the enzyme is to add Threonine amino acid (Thr) to threonine specific tRNA (tRNA-thr) a necessity prep for the protein synthesis pathway. Below displays the overview of the Aminoacylation rxn [1]TARS adds amino acid to tRNA by a two-step mechanism. First the enzyme binds to both and in the catalytic domain to perform an adenylation reaction in which pyrophosphate is released as a byproduct. This is then follow up by a transferring Thr from Adenosine monophosphate molecule to 3'OH site of tRNA-thr. [2] Image below demonstrates the arrow pushing occuring to generate threonine bound tRNA-thr. 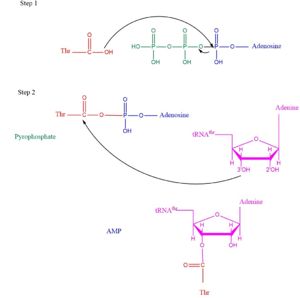 Arrow pushing of Aminoacylation rxn.[3]
Structural highlightsStructural insight into AminoacylationEvolutionarily related proteinsList to available structuresReferences
This is a sample scene created with SAT to by Group, and another to make of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes.
| ||||||||||||

