This is a default text for your page Gisele A. Andree/Sandbox 1. Click above on edit this page to modify. Be careful with the < and > signs.
You may include any references to papers as in: the use of JSmol in Proteopedia [1] or to the article describing Jmol [2] to the rescue.
Function
Dihydropyrimidine Dehydrogenase (DPD) is the first enzyme in pyrimidine degradation pathway. It catalyzes the reduction of 5,6-double bond to obtain dihydropyrimidine.
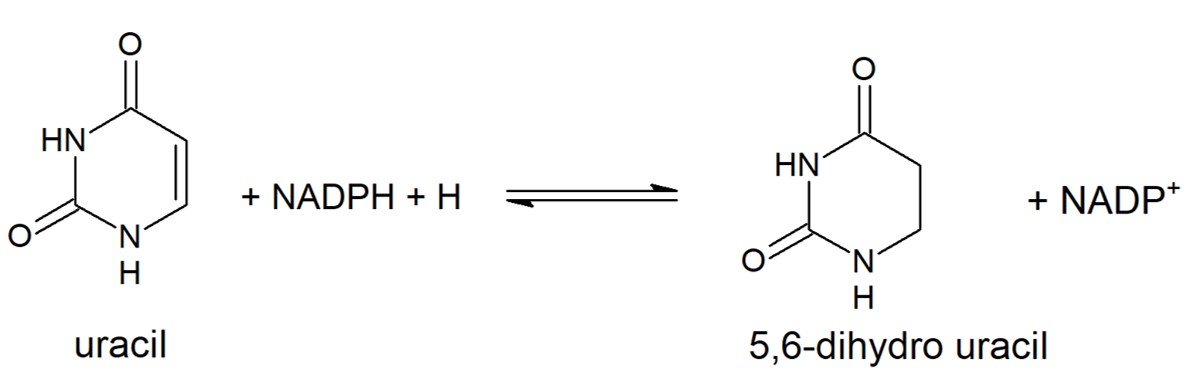
Reduction of Uracil to form 5,6-dihydro uracil. This reaction is catalyzed by eukaryotic DPD. Other pyrimidines can take the place of uracil in this reaction and will be metabolized in the same way.
Disease
5-fluorouracil (5-FU) is a drug used to treat a variety of cancers as it has wide anti-tumor activity & works well alongside other chemotherapy drugs. In the human liver 80-85% of 5-FU is catabolized into inactive, and potentially toxic, metabolites by DPD. Only 1-3% of the original dose proceeds through anabolic pathways to create active cytotoxic complexes. The active complexes inhibit DNA synthesis and the processing and function of RNA processing thus producing a deleterious effect on both healthy and cancerous cells.
DPD decreases effectivity of drug thus requires a very high dosages, leading to major side effects. Luckily, inhibitors are in development and some are in clinical trials.
Relevance
Structural highlights
This is a sample scene created with SAT to by Group, and another to make of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes.

