Journal:Acta Cryst F:S2053230X19001213
From Proteopedia

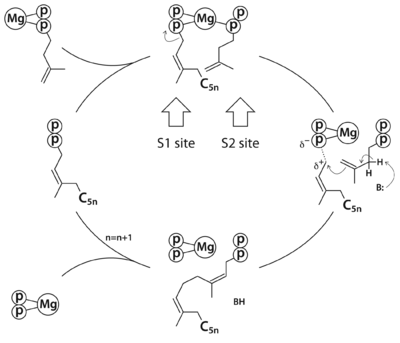
Substrate analogue complex structure of Mycobacterium tuberculosis decaprenyl diphosphate synthaseTzu-Ping Ko, Xiansha Xiao, Rey-Ting Guo, Jian-Wen Huang, Weidong Liu, Chun-Chi Chen [1] Molecular Tour . The two monomers in an asymmetric unit of the MtDPPS crystal are shown as ribbon diagrams. The β-strands are named A-F and the α-helices numbered 1-7 from N to C terminus. They are colored yellow/red for one subunit and magenta/cyan for the other. . The MtDPPS dimer is superimposed on itself with the two polypeptide chains switched. The protein is colored cyan/green in one dimer and pink/yellow in the other, and so are the side chains and the ligands, which are shown as stick models. Mg and water molecules are shown as spheres, and the coordinate bonds as dashed lines. Location of the S1 and S2 site as well as the nearby helices α1/α2 and strand βB are also indicated. When the S1 and S2 substrates and Mg are properly bound for catalysis, the . The . In the absence of both the S2 substrate and Mg, Arg292* turns to bind directly to Asp76, which is no longer engaged in Mg-coordination. The side chain of Arg292* binds to the β-phosphate of the S1 substrate in this conformation, and in the other it is also close to the β-phosphate of the S2 substrate. . 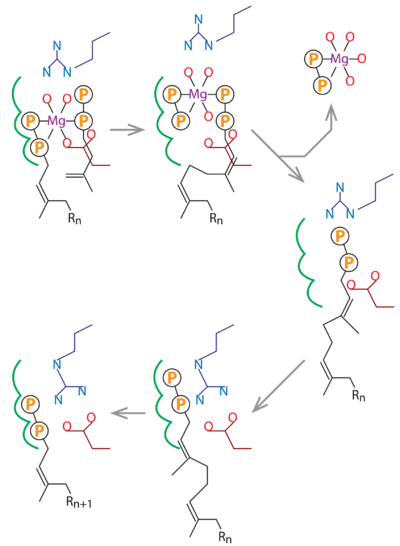 In this schematic diagram, the side chains of Asp76 and Arg292 are colored dark red and dark blue. The three subsites for the alternative binding modes of the S1 substrate are indicated by green curves. Other bonds, including the Mg-coordinates, are in black. Rn stands for a group of n consecutive isoprene units (C5n). References
| |||||||||||