Function
Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase (PPIase) interconverts cis and trans isomers of proline. PPIase functions as a protein folding chaperone.
- PPIase Pin1 isomerizes phospho-serine/threonine proline motifs[1]. The deregulation of Pin1 may be involved in cancer and Alzheimer Disease. Pin1 consists of 2 domains: the WW domain recognizes the pSer/pThr Pro motif and the PPIase domain contains the catalytic site.
- PPIase PinA is an archaeal parvulin-like PPIase.
- PPIase Mip (macrophage infectivity potentiator) is required for optimal infection of macrophages by some parasites[2].
- PPIase SlyD acts as a chaperone and speeds up protein folding.
- PPIase SlpA is a 2-domain protein containing an FK506-binding domain and a PPIase domain and a small insert-in-flap domain which acts as a chaperone[3].
For various types of PPIase see:
• Cyclophilin
• FK506 binding protein for SlyD
• The Escherichia coli sensitive to lysis D (SlyD) protein
• Multifaceted SlyD from Helicobacter pylori: implication in NiFe hydrogenase maturation
Disease
Mutations in PPIase genes are associated with age-related diseases like cardiovascular diseases, atherosclerosis, diabetes type II, chronic kidney disease, neurodegredation, cancer and age-related macular degeneration[4].
Structural highlights
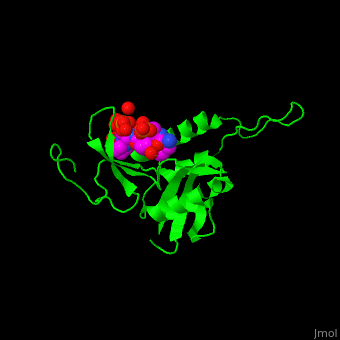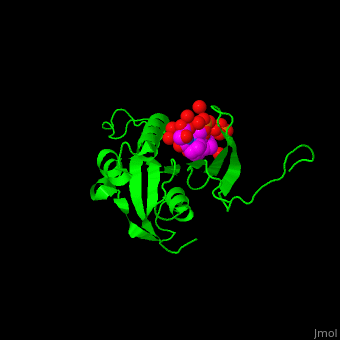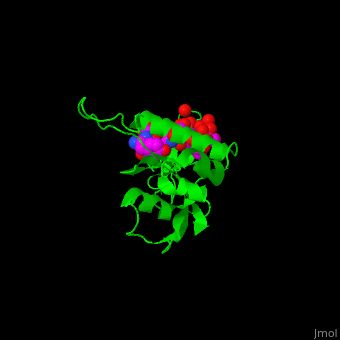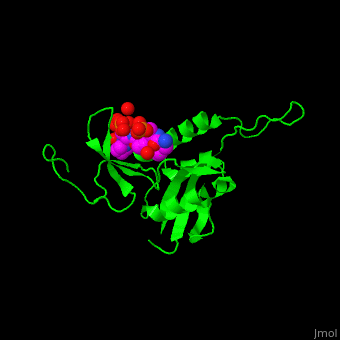
The phosphoserine containing peptide found in the heptad repeat of RNA polymerase II large subunit interacts with the WW domain of PPIase Pin1[5]. . Water molecules are shown as red spheres.
3D Structures of peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase
Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase 3D structures