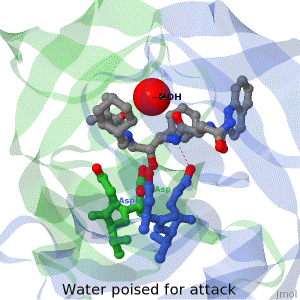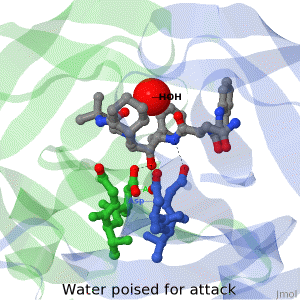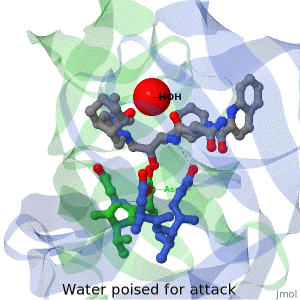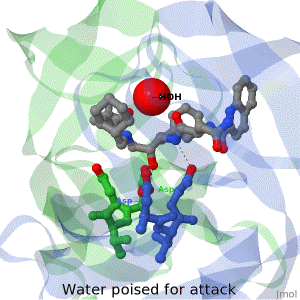
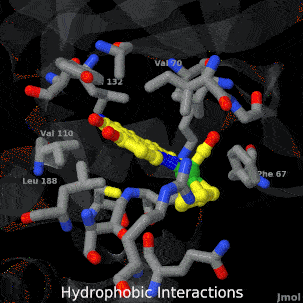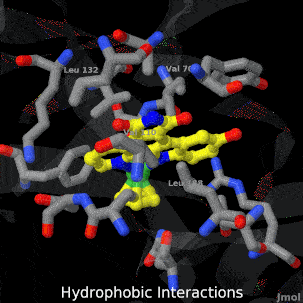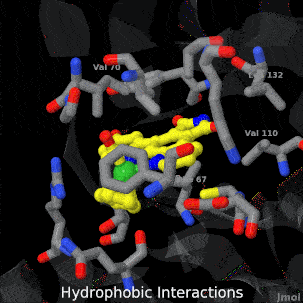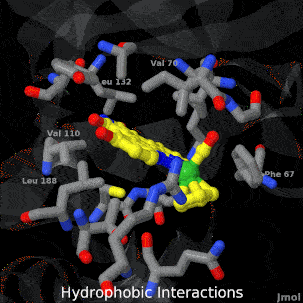
Main Page
From Proteopedia
|
ISSN 2310-6301
As life is more than 2D, Proteopedia helps to bridge the gap between 3D structure & function of biomacromolecules Proteopedia presents this information in a user-friendly way as a collaborative & free 3D-encyclopedia of proteins & other biomolecules.
| ||||||||
| Selected Research Pages | In Journals | Education | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
||||||
|
How to add content to Proteopedia Who knows ... |
Teaching strategies using Proteopedia |
|||||||
| ||||||||