ACE2/structural biology project
From Proteopedia
|
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) is a type I integral membrane protain. ACE2 is known to be localized in various organs such as lungs, stomach, small intestine, heart, testis and kidney [1]. It is also a component of the renin-angiotensin system (RAS), which plays mediating role in cardiovascular system [2]. The most recent studies shows, that the ACE2 has been identified as a functional receptor for the acute respiratory syndrome viruses [3][4].
Contents |
Function
ACE2 is a carboxypeptidase, which plays role in renin-angiotensin system (RAS)[5] as an antagonist of the ACE. Angiotensin II plays the central role in the RAS; and its production is catalized by ACE. ACE2 inactivates peptide angiotensine II (Ang II) by removing the C-terminal amino acid phenylalanine [6] Both ACE and ACE2 cleave Ang I, but instead of bechave as dipeptidase, The N-terminal domain of ACE2 cleaves Angiotensin I to produce Ang-(1-9), by removing the single C-terminal Leu residue [7].
Coexpression of ACE2 with B0AT1 plays role in amino acid transport. Specific interaction of both ACE2 and B0AT1 inrease expression of the B0AT1[8] Also ACE2 functions as a chaperone for the B0AT1[9].
Over- and/or underrepresented expression of the enzyme define a critical role in cardiovascular diseases [10].
ACE2 facilitates HCoV-NL63[11], SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 entry, that is causing COVID-19 epidemic[12]. B0AT1 interacts with aminopeptidase N, another coronavirus receptor [13], but possibility of blocking of the ACE2 cleavage and suppressing of the SARS-CoV-2 infection will have been studying[14]
Structure
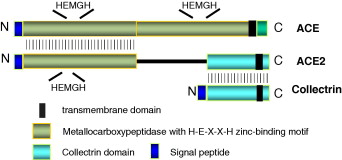
The protein has considerable homology to human angeotensin converting enzyme (ACE); Single catalitic domain (amino acids 147-555) residues shared 41,8% identity with the human ACE. C-terminal end (amino acids 614-805) of the ACE2 protein shares 47,8% identity with its paralogue protein called collectrin [15].
Human ACE2 enzyme is composed of 805 amino acids. Extracelular region of the human ACE2 enzyme is composed of an N-terminal zinc metallopeptidase domain and a C-terminal collectrin-like domain ended with a transmembrane helix.
Location
ACE2 gene is located in Chromosome X on forward strand.
References
- ↑ Hamming I, Timens W, Bulthuis ML, Lely AT, Navis GJ, van Goor H. Tissue distribution of ACE2 protein, the functional receptor for SARS coronavirus. A first step in understanding SARS pathogenesis. J Pathol. 2004 Jun;203(2):631-7. PMID:15141377 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/path.1570
- ↑ Donoghue M, Hsieh F, Baronas E, Godbout K, Gosselin M, Stagliano N, Donovan M, Woolf B, Robison K, Jeyaseelan R, Breitbart RE, Acton S. A novel angiotensin-converting enzyme-related carboxypeptidase (ACE2) converts angiotensin I to angiotensin 1-9. Circ Res. 2000 Sep 1;87(5):E1-9. PMID:10969042
- ↑ Prabakaran P, Xiao X, Dimitrov DS. A model of the ACE2 structure and function as a SARS-CoV receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004 Jan 30;314(1):235-41. doi:, 10.1016/j.bbrc.2003.12.081. PMID:14715271 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2003.12.081
- ↑ Yan R, Zhang Y, Li Y, Xia L, Guo Y, Zhou Q. Structural basis for the recognition of the SARS-CoV-2 by full-length human ACE2. Science. 2020 Mar 4. pii: science.abb2762. doi: 10.1126/science.abb2762. PMID:32132184 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.abb2762
- ↑ Burrell LM, Johnston CI, Tikellis C, Cooper ME. ACE2, a new regulator of the renin-angiotensin system. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2004 May-Jun;15(4):166-9. doi:, 10.1016/j.tem.2004.03.001. PMID:15109615 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tem.2004.03.001
- ↑ Clayton D, Hanchapola I, Thomas WG, Widdop RE, Smith AI, Perlmutter P, Aguilar MI. Structural determinants for binding to angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) and angiotensin receptors 1 and 2. Front Pharmacol. 2015 Jan 30;6:5. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2015.00005. eCollection, 2015. PMID:25688208 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2015.00005
- ↑ Donoghue M, Hsieh F, Baronas E, Godbout K, Gosselin M, Stagliano N, Donovan M, Woolf B, Robison K, Jeyaseelan R, Breitbart RE, Acton S. A novel angiotensin-converting enzyme-related carboxypeptidase (ACE2) converts angiotensin I to angiotensin 1-9. Circ Res. 2000 Sep 1;87(5):E1-9. PMID:10969042
- ↑ Kowalczuk S, Broer A, Tietze N, Vanslambrouck JM, Rasko JE, Broer S. A protein complex in the brush-border membrane explains a Hartnup disorder allele. FASEB J. 2008 Aug;22(8):2880-7. doi: 10.1096/fj.08-107300. Epub 2008 Apr 18. PMID:18424768 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1096/fj.08-107300
- ↑ Gheblawi M, Wang K, Viveiros A, Nguyen Q, Zhong JC, Turner AJ, Raizada MK, Grant MB, Oudit GY. Angiotensin Converting Enzyme 2: SARS-CoV-2 Receptor and Regulator of the Renin-Angiotensin System. Circ Res. 2020 Apr 8. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.317015. PMID:32264791 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.317015
- ↑ Patel VB, Zhong JC, Grant MB, Oudit GY. Role of the ACE2/Angiotensin 1-7 Axis of the Renin-Angiotensin System in Heart Failure. Circ Res. 2016 Apr 15;118(8):1313-26. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.307708. PMID:27081112 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.307708
- ↑ Hofmann H, Pyrc K, van der Hoek L, Geier M, Berkhout B, Pohlmann S. Human coronavirus NL63 employs the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus receptor for cellular entry. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 May 31;102(22):7988-93. Epub 2005 May 16. PMID:15897467 doi:http://dx.doi.org/0409465102
- ↑ Yan R, Zhang Y, Li Y, Xia L, Guo Y, Zhou Q. Structural basis for the recognition of the SARS-CoV-2 by full-length human ACE2. Science. 2020 Mar 4. pii: science.abb2762. doi: 10.1126/science.abb2762. PMID:32132184 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.abb2762
- ↑ Jando J, Camargo SMR, Herzog B, Verrey F. Expression and regulation of the neutral amino acid transporter B0AT1 in rat small intestine. PLoS One. 2017 Sep 15;12(9):e0184845. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0184845., eCollection 2017. PMID:28915252 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0184845
- ↑ Yan R, Zhang Y, Li Y, Xia L, Guo Y, Zhou Q. Structural basis for the recognition of the SARS-CoV-2 by full-length human ACE2. Science. 2020 Mar 4. pii: science.abb2762. doi: 10.1126/science.abb2762. PMID:32132184 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.abb2762
- ↑ Zhang Y, Wada J. Collectrin, a homologue of ACE2, its transcriptional control and functional perspectives. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007 Nov 9;363(1):1-5. doi:, 10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.08.136. Epub 2007 Aug 31. PMID:17825789 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.08.136