User:Sumit Kamat/Sandbox Reserved 901
From Proteopedia
Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase 2A KMT2A
OverviewHistone-lysine N-methyltransferase 2A (KMT2A) known as mixed-lineage leukemia 1 (MLL-1) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the KMT2A gene. KMT2A gene is a histone methyltransferase which are histone modifying enzymes which catalyze the transfer of methyl groups to lysine and arginine residues of histone proteins. The KMT2A gene is a positive global regulator of gene transcription and comprises of transactivation domain 9aaTAD which is involved in the epigenetic maintenance of transcriptional memory [1]. The KMT2 family can mono-, di- and trimethylates histone H3K4. This family of enzymes is found within a macromolecular complex known as the COMPASS family and are highly conserved from yeast to human [2].
FunctionThe KMT2A gene encodes a protein which is contains multiple conserved domains. KMT2A gene encodes a transcriptional coactivator that plays an important role in regulating gene expression during early development and hematopoiesis. Out of the many domains, SET domain is responsible for its histone H3 lysine 4 (H3K4) methyltransferase activity which mediates chromatin modifications associated with epigenetic transcriptional activation [3].The SET1 and MLL (KMT2) methyltransferases are conserved from yeast through humans. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome encodes a single H3K4 methyltransferase, Set1, whereas humans possess at least six homologs: SET1a, SET1b and MLL1-4. Unlike many SET domain enzymes, SET1 and MLL KMTs display very weak activity toward H3K4 and require additional subunits to attain maximal activity [4].MLL-1 has a defined role in mammalian development, where it has been shown to be required for the regulation of important homeobox (Hox) genes and therefore is essential for early patterning in the embryo. In acute myeloid and lymphoid leukemia the MLL1 gene is frequently targeted in oncogenic gene translocations, leading to the expression of chimeric fusions between the amino-terminal 1400 residues of MLL1 and one of over 50 partner genes. MLL1 translocations are more prevalent in childhood leukemias and in therapy-related cases, where they are associated with a poor prognosis [5].
Structural AnalysisMLL-1 is a 431-kDa protein to be a structural and functional homolog of the Drosophila trithorax (TRX) protein. Two domains are highly conserved between MLL and TRX consist of a carboxy-terminal SET (Su(var)3-9, enhancer-of-zeste, and trithorax) domain and internal plant homeodomain (PHD) fingers. Both domains are found in many chromatin-associated transcriptional regulators and are thought to function either directly in chromatin modification or as protein-protein interaction surfaces for the recruitment of chromatin-modifying machinery [6].
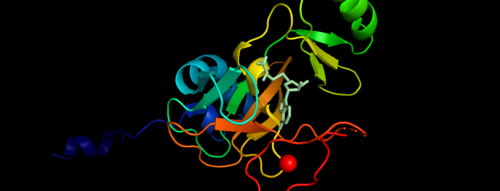
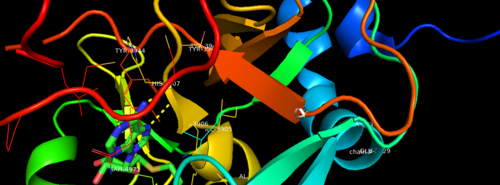
Sequence HighlightsImage:2w5y sequence chain final Figure 3. Secondary structure of KMT2A SET Domain with the cofactor product S-Adenosylhomocysteine. Relevance</StructureSection> References
| ||||||||||||