3D structure representation of the Spike glycoprotein related to the SARS-CoV-2 [1] [2].
Introduction
The Spike protein is related to the novel coronavirus pandemic discovered in 2019. The virus is named as the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and it belongs to the β coronavirus family. The SARS-CoV-2 is a single stranded RNA with 29,881bp length, which encodes for 9860 amino acids. It is compose of two proteins: the structural and non-structural proteins. The structural proteins are S,E,M and N ; whiles as the non-structural proteins are encoded on the ORF regions[3].
The Spike Protein
The S-protein is a structural protein extends from the viral membrane and it is uniformly arranged as a trimer on the surface to give the crown-like appearance of the SARS-Co
V-2. The Spike protein is 14-1255bp long, which mediates a receptor binding Val367 and fusion of the virus and a cellular membrane [4]. Is also gives the virus its name in Latin as "Corona".
Domains
The S-protein of the SARS-CoV-2 has two main subunits , an S1 and S2 subunits NTD-CT . The S1 subunit is located on residue #14–685 ( contains the NTD, blue label) and interact with human AEC2 by attaching its virion to the cell membrane by interacting with host receptor. The S2 subunit is located on residue #686–1273 ( contains the CT, red label ) which serves as the fusion protein of the virus [5].
Activation of S-protein
Before the Spike protein can be activated , it has to be cleaved by the protease Furin protein ALA 668 . This 2D image below shows the schematic cleavage of the S-protein before and after it enters the host cell
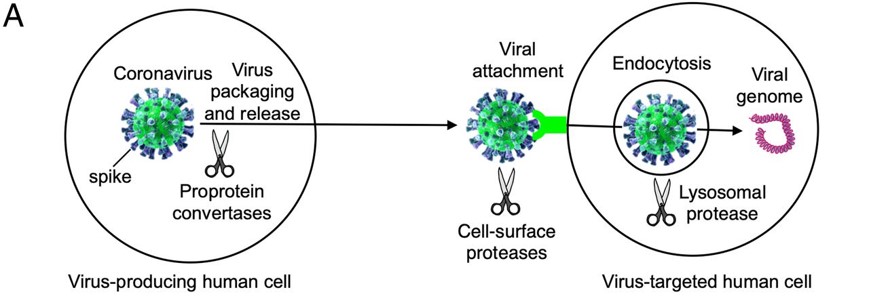 [6]
[6]
The Mechanism of the Spike Protein
LYS 187
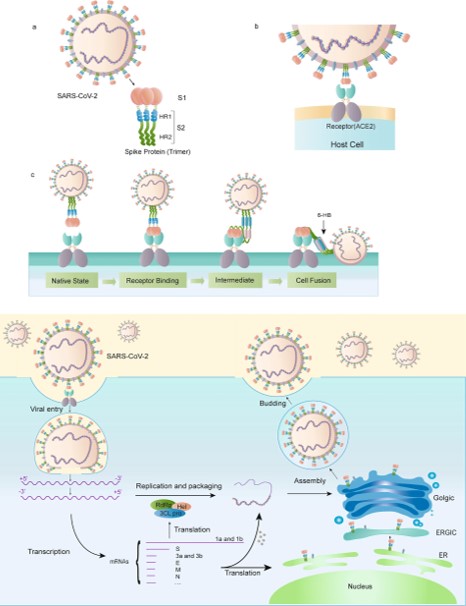 [7]
[7]
Mutation
The most studied mutation site of the S-protein is at residue 614 which encodes for the amino acid Aspartic acid (D) D614 and is normally changed to Glycine (G). And this form of mutation causes the enhancement of the viral transmission [8].
Structural highlights
These are the structural 3D representations of the s-protein showing the two subunits , the binding regions to its receptor human ACE2 , Mutation site , RBD site and cleavage site respectively. NTD-CT .Val367 . D614 . LYS 187 .ALA 668


