Function of your Protein
are cell wall proteins responsible for for the binding of a bacteria or fungi to its host. My epithelial adhesin is part of the Candida glabrata, Candidiasis are any type of fungal infections resulting from Yeast (candida). Their N-terminal domains are endowed with a calcium-dependent lectin activity. This feature allows the yeast cells to adhere to host cells by establishing multiple interactions with the glycans expressed on their cell membrane. My Protein binds to . Once the fungi binds to its host it can then release enzymes through its hyphae that help it absorb nutrients from the host.
Biological relevance and broader implications
Epithelial Adhesins are important for fungi because they help the organism bind to the host so they can live, gain nutrients and maintain its steady state. Candida Glabrata which house these epithelial adhesins are the 2nd major cause of clinical candidiasis, It is most prevalent in vaginal infections but can even cause systemic infections by entrance of the fungal cells in the bloodstream (Candidemia), especially prevalent in immunocompromised patients. it is important to study proteins like epithelial adhesins so we can better understand how fungi and other organisms infect the body, by understanding the role of these proteins we can begin to work on combat methods and long term immunity.
Important amino acids
i: DcisD = DD or asp 196,197 hydrogen bond with Gal b, metal interactions
with Ca+ that also has metal interactions with Gal b
ii: Asn 256 is asparagine has metal interactions with ca+ and Gal b
iii: Asp 258 metal interaction with gal b
iv: Arginine 257 hydrogen bonds with ligand gal b, cation pi interactions with
trp 110
v: His 260 has metal interactions with Gal b
vi: Cys 109 and 151 disulfide bond and hydrogen bond with N-acetyl-d-
glucosamine (GlcNAc)

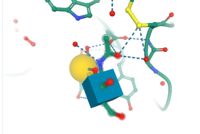
Structural highlights
My protein is a epithelial adhesin protein bonded to a Galactose beta 1-3 N-acetyl-D-Glucosamine, it contains 3 to 5 small and a core of anti parralel beta sheets also known as the . all of the important catalytic amino acids bind to the ligand by hydrogen bonds with the ligand itself or metal interaction with Ca+ its also contains a disulfide bond binding two loops together that are crucial in ligand affinity. These two loops connected by the disulfide bond play a key role in ligand affinity when these loops sequence are changed the protien often accepts a different carbohydrate ligand. Another important structual feature is its lectin calcium dependant qualities, it creates metal interactions with calcium that help bind the Galactose beta 1-3 N-acetyl-D-Glucosamine. the hydrogen bonns and metal interactions allow for less free energy change and easier binding then far from equilibrium reactions that would change the product completely.
Other important features
Other important structures include these two loops are believed to play a major role in carbohydrate/ ligand recognization. loop 2 is believed to hold the CBl2 motif containing the arginine. in my paper they exchanged epa varients and analyzed the different carbohydrates each different loop and CBl2 recognized the loops and CBL2 areas contain variable amino acids with different recognization and function.
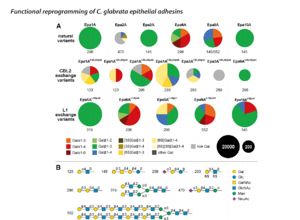
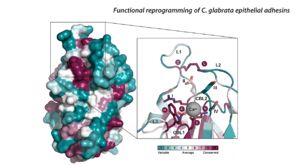
References
<PMID:22349222/>
<https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Candida_glabrata#:~:text=Candida%20glabrata%20is%20a%20species,mating%20types%20are%20commonly%20found./>
https://www.rcsb.org/3d-view/4CP1?preset=oligoInteraction&sele=B
https://www.rcsb.org/structure/4cp1
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22349222/




