Function
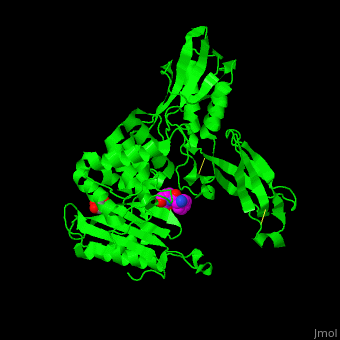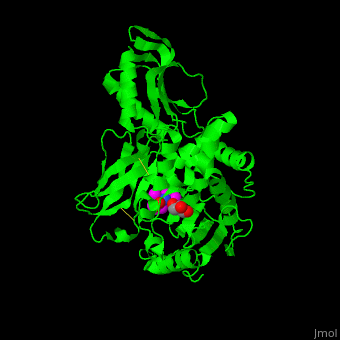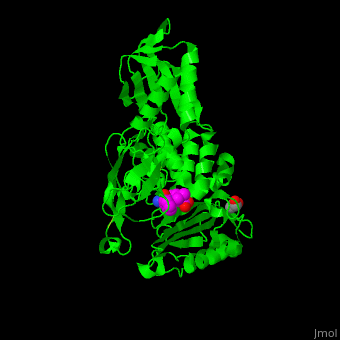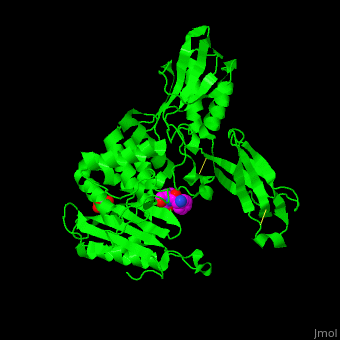
Penicillin-binding protein or peptidoglycan d,d-transpeptidase or D-alanyl-D-alanine carboxypeptidase (PBP) is a bacterial protein which binds antibiotics. There are several PBPs in each organism. PBPs are involved in the synthesis of bacterial cell wall[1]. The PBP are classified to high-molecular weight and low-molecular weight groups. PBP 3 is also named FtsI.
For Mycobacterium tuberculosis PBP complex with penicillin see Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Transpeptidase Domain.
Relevance
PBP inhibition by antibiotics leads to irregularities in the cell wall and eventual bacterial death[2].
See also How B-lactam drugs work.
Structural highlights
E. coli PBP structure shows a distinct . The contains the [3]. Water molecules are shown as red spheres.
3D structures of penicillin-binding protein
Penicillin-binding protein 3D structures