Sandbox Reserved 1750
From Proteopedia
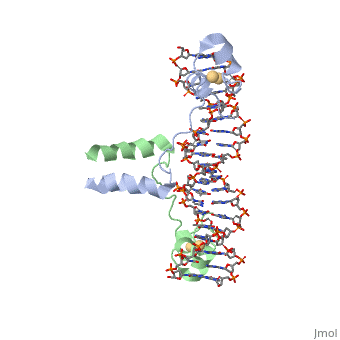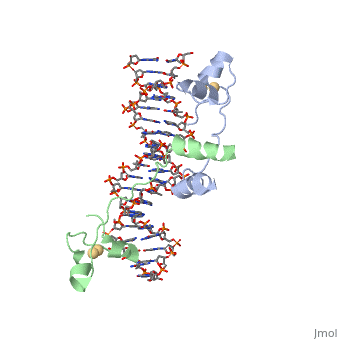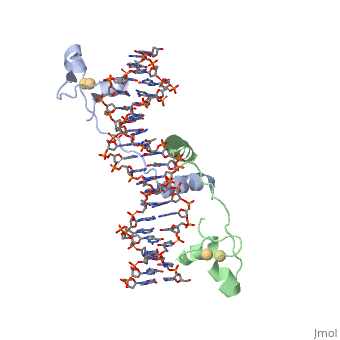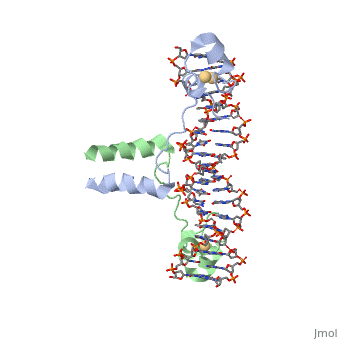
Displayed</scene></scene>==DNA RECOGNITION BY GAL4: STRUCTURE OF A PROTEIN/DNA COMPLEX==
| |||||||||||
Contents |
STRUCTURE OF Cas9 IN STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS IN COMPLEX WITH gRNA
Cas9 Overview
CRISPR is a bacterial immune response to bacteriophages to prevent subsequent infections and is a form of acquired immunity. Within the CRISPR system, Cas9 is a protein responsible for cutting the viral DNA rendering it inert. structure in Staphylococcus aureus (SaCas9) utilizes a single stranded guide RNA (sgRNA) to bind the target DNA that will be cut. The target DNA must also have a PAM sequence to bind to Cas9 to be cut. Cas9 has four main mechanisms that are important for successful cleavage including recognition of the sgRNA-target heteroduplex, recognition of the PAM sequence, recognition of the sgRNA scaffold, and endonuclease activity by HNH and RuvC.
Recognition of the sgRNA-target heteroduplex
The recognition of the sgRNA-target heteroduplex in Cas9 begins by inserting itself into the central channel between the REC and NUC lobes. The REC lobe interacts with the seed region of the sgRNA (C13-C20) as well as the PAM distal region (A3-U6) through the phosphate backbone. The seed region is in the A-form confirmation so it can bind the target DNA. The target DNA binds to the REC loop and RuvC domain for the proper conformation for base paring between the target DNA and sgRNA.
Recognition of the PAM seequence
For the recognition of the PAM sequence, the target DNA with the PAM sequence (5’-NNGRRN-3’) is bound to SaCas9 through bidentate hydrogen bonds as well as direct and water mediated hydrogen bonds through the major groove in the PI domain. The WED domain recognizes the minor groove phosphate backbone of the duplex.
Recognition of the sgRNA scaffold
The SaCas9 recognizes the sgRNA scaffold within the REC and WED domains. The WED domain contains five stranded beta sheets flanked with four alpha helices to allow binding of the repeat:anti-repeat duplex. REC lob binds the scaffold and secures it into the SaCas9.
Endonuclease Activity of Cas9
Finally, RuvC and HNH are in endonuclease activity. RuvC uses a two-metal ion mechanism of manganese to cleave the non-target DNA and causes a conformational change in L1. This conformational change leads to the phosphate group of the target strand to be cleaved by HNH. HNH includes a beta beta alpha metal fold and uses a one metal ion mechanism to cleave the target DNA.