This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
User:Daniel Key Takemoto/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
Structure and functions
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1515737112
N-terminal domain
RGG motif
Different domains and motifs mediate the RNA binding mechanism and the exon 15-encoded RGG (arginine - glycine - glycine) motif is one of them. The RGG motif is well conserved in vertebrates.To easily represent the RGG motif binding to a RNA, this motif will be highlitghted in the scene . Several tetrads can stack in a single G-quadruplex structure and be stabilized further by potassium cations, in the case of FMRP targets, whereas destabilized by lithium cations. FMRP RGG motifs seem to prefer binding to specific structures, not linear motifs. Therefore, the understanding of the interaction RGG-RNA is important for the comprehension of the FMRP and FXS.
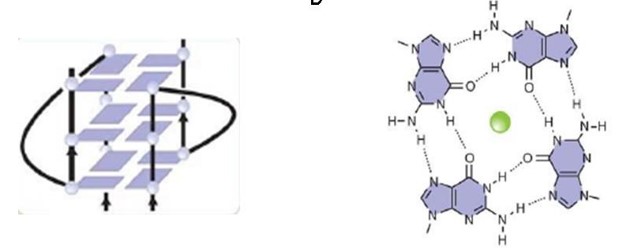 A motif that is going to be explored is the RGG motif, that the protein uses to bind to guanine G-quadruplexes a structure that consists of nucleic acid folding in which four guanines arrange in a planar conformation stabilized by Hoogsteen-trype hydrogen bonds, named tetrad.
A motif that is going to be explored is the RGG motif, that the protein uses to bind to guanine G-quadruplexes a structure that consists of nucleic acid folding in which four guanines arrange in a planar conformation stabilized by Hoogsteen-trype hydrogen bonds, named tetrad.
Associated diseases
Trinucleotides repeats (CGG) are located in CpG islands in the 5' untranslated region (UTR) of the gene related to the expression of the gene. Individuals carrying up to 44 repeats of trinucleotides are of common aleles. Individuals that have between 44 and 55 repeats are known to carry the premutation, usually associated with FXTAS and PFO1. However, when the repeat expansion is above 55 the individual is carrying the full mutation, which leads to the silencing of the gene, due to methylation, therefore there is absence or reduced levels of the FMRP, causing abnormal synaptic development and symptons associated with the FXS.
Relevance
Structural highlights
This is a sample scene created with SAT to by Group, and another to make of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes.
