We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
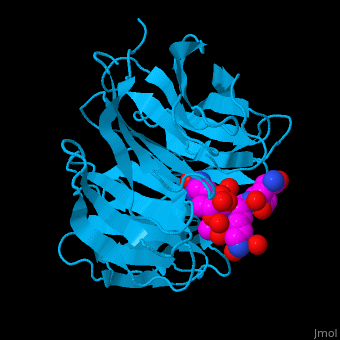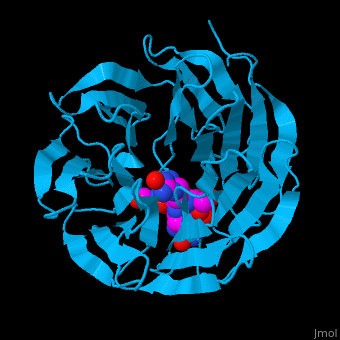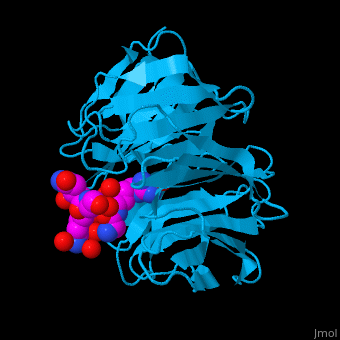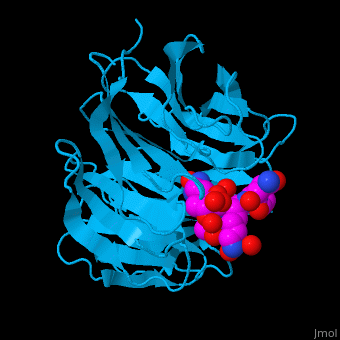
WD repeat-containing protein
From Proteopedia
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Li D, Roberts R. WD-repeat proteins: structure characteristics, biological function, and their involvement in human diseases. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2001 Dec;58(14):2085-97. PMID:11814058
- ↑ Gan Q, Thiebaud P, Theze N, Jin L, Xu G, Grant P, Owens GK. WD repeat-containing protein 5, a ubiquitously expressed histone methyltransferase adaptor protein, regulates smooth muscle cell-selective gene activation through interaction with pituitary homeobox 2. J Biol Chem. 2011 Jun 17;286(24):21853-64. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.233098. Epub, 2011 Apr 28. PMID:21531708 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.233098
- ↑ Sullivan PM, Zhou X, Robins AM, Paushter DH, Kim D, Smolka MB, Hu F. The ALS/FTLD associated protein C9orf72 associates with SMCR8 and WDR41 to regulate the autophagy-lysosome pathway. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2016 May 18;4(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s40478-016-0324-5. PMID:27193190 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s40478-016-0324-5
- ↑ Rapiteanu R, Davis LJ, Williamson JC, Timms RT, Paul Luzio J, Lehner PJ. A Genetic Screen Identifies a Critical Role for the WDR81-WDR91 Complex in the Trafficking and Degradation of Tetherin. Traffic. 2016 Aug;17(8):940-58. doi: 10.1111/tra.12409. Epub 2016 May 25. PMID:27126989 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/tra.12409
- ↑ van der Weegen Y, Golan-Berman H, Mevissen TET, Apelt K, González-Prieto R, Goedhart J, Heilbrun EE, Vertegaal ACO, van den Heuvel D, Walter JC, Adar S, Luijsterburg MS. The cooperative action of CSB, CSA, and UVSSA target TFIIH to DNA damage-stalled RNA polymerase II. Nat Commun. 2020 Apr 30;11(1):2104. PMID:32355176 doi:10.1038/s41467-020-15903-8
- ↑ Tullio-Pelet A, Salomon R, Hadj-Rabia S, Mugnier C, de Laet MH, Chaouachi B, Bakiri F, Brottier P, Cattolico L, Penet C, Begeot M, Naville D, Nicolino M, Chaussain JL, Weissenbach J, Munnich A, Lyonnet S. Mutant WD-repeat protein in triple-A syndrome. Nat Genet. 2000 Nov;26(3):332-5. PMID:11062474 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/81642
- ↑ Schuetz A, Allali-Hassani A, Martin F, Loppnau P, Vedadi M, Bochkarev A, Plotnikov AN, Arrowsmith CH, Min J. Structural basis for molecular recognition and presentation of histone H3 by WDR5. EMBO J. 2006 Sep 20;25(18):4245-52. Epub 2006 Aug 31. PMID:16946699
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Joel L. Sussman, Jaime Prilusky