Introduction
Proline Peptidase Overview
History
Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV's role in the inactivation of incretin hormones was discovered in the 1990s. Animal studies were conducted in the late 1990s, followed by human studies in the early 2000s. The first DPPIV inhibitors (sitagliptin, vildagliptin, alogliptin, saxagliptin, and linagliptin) were approved starting in 2006, and now serve as monotherapy or add-on to other therapies in a glucose-lowering capacity. [1] Since their approval, there have been multiple long-term trials to continue exploring the long-term effects of these medications. It is known that gliptins directly impact the pancreas, kidney, heart, and vessels. The most investigated thus far is the effects of gliptins on real and cardiovascular functioning. [2] Results of phase II and III trails indicated that gliptins did not harm the cardiovascular system. A meta-analysis implicated two possible beneficial effects for patients treated with these medications: a reduction in cardiovascular effects and a direct renoprotective effect. [3]
Function
DPPIV, a moonlighting protein, has been implicated in many functions and diseases of the body including glucose metabolism, cardiovascular disease, the stress response, autoimmune diseases (i.e. HIV/AIDS), inflammation, and tumor biology. [4] [5] [6] The active site functions in two ways: it can bind inhibitors and it can truncate substrates. Inhibitors inhibit DPPIV via competitive inhibition, binding to the active site but are not degraded, so they remain bound and block the enzymatic activity. Substrates are truncated by DPPIV by temporarily forming a covalent bond and ultimately being released in two pieces (the first two residues and the truncated protein).
Structure
Something about interactions...
[7]
Overview
NEED TO INSERT TEXT ABOUT THE BINDING POCKETS TO GO WITH MY SCENE
will insert something to go with saxagliptin scene below:
please work
DPPIV is found in two forms in the body: a membrane bound monomer and a blood soluble dimer. All structural renderings of DPPIV start at the 39th residue, meaning it does not include the intracellular domain, transmembrane region, and part of the cleavage site. The monomer has 4 domains: DPPIV cleavage stalk, beta propeller, cystine-rich region, and the catalytic domain. The DPPIV beta propellor is notable as it differs from all the other enzymes in the dipeptidyl peptidase family. In all other DPPs the beta propeller has ligand gating potential; however, the is an asymmetrical 7 blade propeller that does not function as a ligand gate by rather acts as a binding site which allows DPPIV to conjugate with Adenosine Deaminase. [8]
The contains 6 cystine residues (C385, C394, C444, C447, C454, C472) that make that play a critical role in the tertiary structure and therefore function of the DPPIV enzyme. [9]
The includes the S1 binding pocket and S2 binding pocket. The S1 binding pocket contains hydrophobic residues (INSERT RESIDUES) (INSERT SCENES???)
Catalytic Triad
[7]
Mechanism
maybe include something about stabilization from the oxyanion hole??
Once a substrate is bound in the active site, DPPIV utilizes a covalent catalysis mechanism to cleave the substrate at the penultimate position. Asp708 of the (Ser630, His 740, Asp708) pulls electron density from His740 allowing the histidine to pull electron density from Ser630, making serine a stronger nucleophile. The water molecule attacks the carbonyl carbon, breaking the newly formed covalent bond, and releasing the first two residues of the starting substrate. The active site resets.
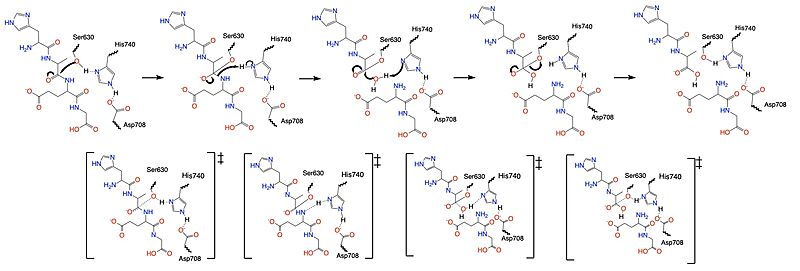
Figure 5. Mechanism of the catalytic triad of DPPIV.
Inhibitors
Gliptins, a class of oral antidiabetic medications, are DPPIV inhibitors. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved the following: sitagliptin, alogliptin, saxagliptin, and linagliptin. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) has approved all of those aforementioned in addition to vildagliptin. Each gliptin is a small molecule (≤ 1000 Da).
Relevance
Diabetes
something about diabetes
HIV/AIDS
Current Scene Student Contributions
Sam
Merritt
Karisma

