[1]
Overview of Esterase
The role in the body this would play based on results. Any potential implications of the enzyme if disrupted based on findings and related enzymes.
Proposed Function
This protein has alpha/beta-hydrolase activity and is of the esterase family. The SPRITE, BLAST, InterPro, and Dali Search along with other bioinformatics analyses consistently matched with carboxylesterases and other esterase-like proteins. SPRITE provided proteins that had similar residues in the active site of the enzyme. Multiple of the matching proteins were esterases and had an RMSD value of <0.5. The RMSD value gives insight into how similar the overlapping sections for the unknown and known proteins are. A value of less than 2 is desired when choosing proteins for reference as a value closer to zero means less deviation between sites.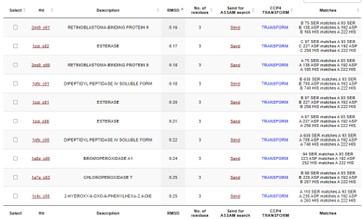
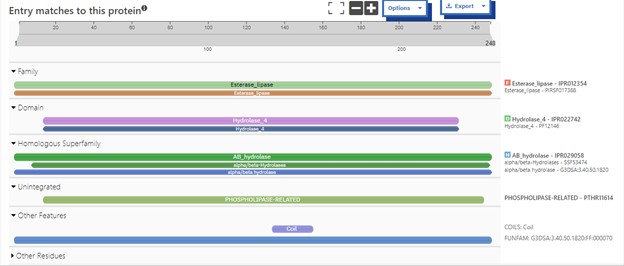
Additional evidence is provided by InteroPro which provided more information about the classification of the protein. As well, the BLAST search gave results of matching proteins and the specific functions of the proteins. All results again matched what was suggested by Sprite and Blast, further solidifying that 4DIU is an esterase with alpha/beta-hydrolase activity.
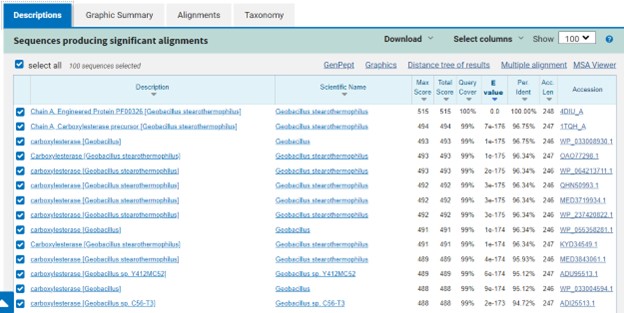
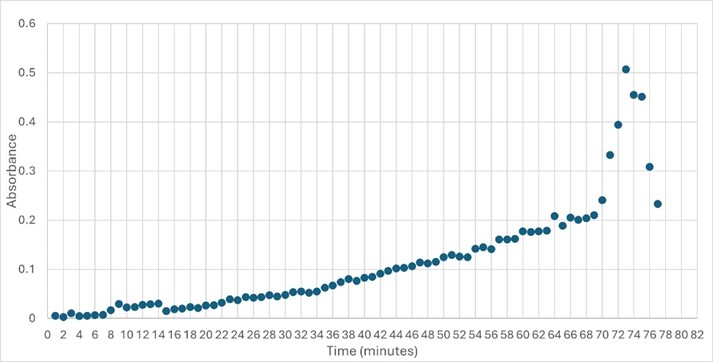
SwissDock and Chimera allowed for protein-ligand docking studies. Many of the highlighted interactions were ester-containing ligands and others were susceptible to hydrolysis. The hydrolase activity of the protein needed to be tested with a substrate known to work with hydrolases. This substrate is p-nitrophenyl acetate PNP when hydrolyzed produces a yellow colored product. The yellow product will lead to the solution absorbing more at 405nm. [2]. This allows for the activity of the enzyme to be tracked by measuring the increase in absorbance over time. The isolated protein was introduced to p-nitrophenyl acetate in a buffer with a determined optimal pH of 6. Enzyme activity was measured via a change in absorbance at 405nm over 80 minutes. The data collected was consistent with that of hydrolases in other studies.
Structural highlights
Highlight the data that helped you come to your conclusion here including any relevant figures. Make sure to include potential substrates and binding sites.



