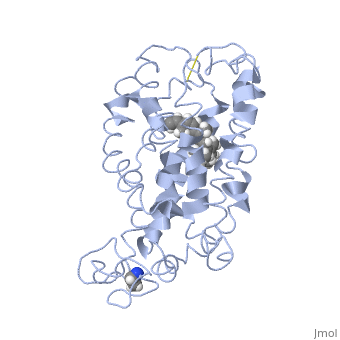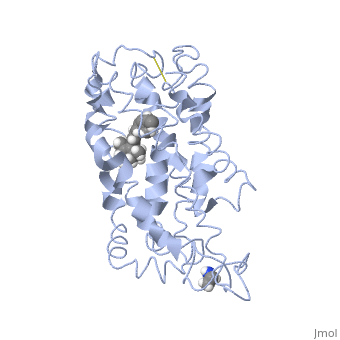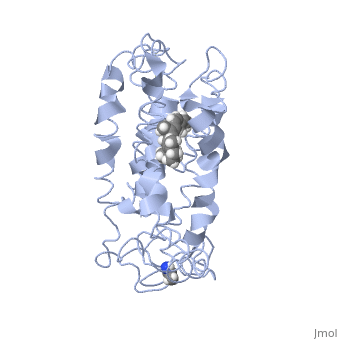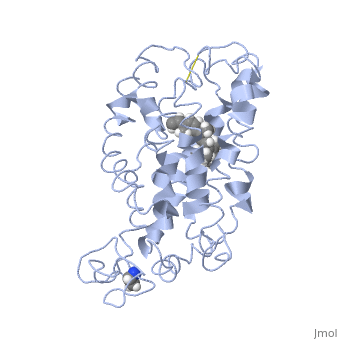
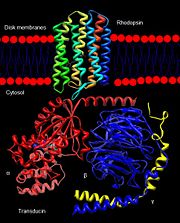
Rhodopsin
From Proteopedia
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Hornak V, Ahuja S, Eilers M, Goncalves JA, Sheves M, Reeves PJ, Smith SO. Light activation of rhodopsin: insights from molecular dynamics simulations guided by solid-state NMR distance restraints. J Mol Biol. 2010 Feb 26;396(3):510-27. Epub 2009 Dec 11. PMID:20004206 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2009.12.003
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 Sakmar TP. Structure of rhodopsin and the superfamily of seven-helical receptors: the same and not the same. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2002 Apr;14(2):189-95. PMID:11891118
- ↑ Tsunoda SP, Prigge M, Abe-Yoshizumi R, Inoue K, Kozaki Y, Ishizuka T, Yawo H, Yizhar O, Kandori H. Functional characterization of sodium-pumping rhodopsins with different pumping properties. PLoS One. 2017 Jul 27;12(7):e0179232. PMID:28749956 doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0179232
- ↑ Yun JH, Li X, Yue J, Park JH, Jin Z, Li C, Hu H, Shi Y, Pandey S, Carbajo S, Boutet S, Hunter MS, Liang M, Sierra RG, Lane TJ, Zhou L, Weierstall U, Zatsepin NA, Ohki M, Tame JRH, Park SY, Spence JCH, Zhang W, Schmidt M, Lee W, Liu H. Early-stage dynamics of chloride ion-pumping rhodopsin revealed by a femtosecond X-ray laser. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Mar 30;118(13). pii: 2020486118. doi:, 10.1073/pnas.2020486118. PMID:33753488 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2020486118
- ↑ PMID:21389988<ref></ref>.
See also Transmembrane (cell surface) receptors
G Protein-Coupled Receptors
Rhodopsin is a member of the superfamily of G protein-coupled receptors that incorporate the activation of G proteins in their modulation of signaling and intracellular actions. Rhodopsin shares similar membrane topology with the members of the superfamily (Family A of the G protein-coupled receptors) which include the seven transmembrane helices, an extracellular N terminus and cytoplasmic C terminus<ref>PMID:15251227</li> <li id="cite_note-Article20">[[#cite_ref-Article20_2|↑]] <strong class="error">Cite error: Invalid <code><ref></code> tag; no text was provided for refs named <code>Article20</code></strong></li> <li id="cite_note-RecentOthers-6">[[#cite_ref-RecentOthers_6-0|↑]] Millar RP, Newton CL. The year in G protein-coupled receptor research. Mol Endocrinol. 2010 Jan;24(1):261-74. Epub 2009 Dec 17. PMID:[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20019124 20019124] doi:[http://dx.doi.org/10.1210/me.2009-0473 10.1210/me.2009-0473]</li> <li id="cite_note-Article10-7">↑ <sup>[[#cite_ref-Article10_7-0|8.0]]</sup> <sup>[[#cite_ref-Article10_7-1|8.1]]</sup> <sup>[[#cite_ref-Article10_7-2|8.2]]</sup> Meng EC, Bourne HR. Receptor activation: what does the rhodopsin structure tell us? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2001 Nov;22(11):587-93. PMID:[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11698103 11698103]</li> <li id="cite_note-Article4-8">↑ <sup>[[#cite_ref-Article4_8-0|9.0]]</sup> <sup>[[#cite_ref-Article4_8-1|9.1]]</sup> Shieh T, Han M, Sakmar TP, Smith SO. The steric trigger in rhodopsin activation. J Mol Biol. 1997 Jun 13;269(3):373-84. PMID:[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9199406 9199406] doi:[http://dx.doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.1997.1035 10.1006/jmbi.1997.1035]</li> <li id="cite_note-Article9-9">↑ <sup>[[#cite_ref-Article9_9-0|10.0]]</sup> <sup>[[#cite_ref-Article9_9-1|10.1]]</sup> <sup>[[#cite_ref-Article9_9-2|10.2]]</sup> <sup>[[#cite_ref-Article9_9-3|10.3]]</sup> <sup>[[#cite_ref-Article9_9-4|10.4]]</sup> <sup>[[#cite_ref-Article9_9-5|10.5]]</sup> <sup>[[#cite_ref-Article9_9-6|10.6]]</sup> <sup>[[#cite_ref-Article9_9-7|10.7]]</sup> <sup>[[#cite_ref-Article9_9-8|10.8]]</sup> Okada T, Ernst OP, Palczewski K, Hofmann KP. Activation of rhodopsin: new insights from structural and biochemical studies. Trends Biochem Sci. 2001 May;26(5):318-24. PMID:[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11343925 11343925]</li> <li id="cite_note-ReferenceArticle-10">↑ <sup>[[#cite_ref-ReferenceArticle_10-0|11.0]]</sup> <sup>[[#cite_ref-ReferenceArticle_10-1|11.1]]</sup> Okada T, Sugihara M, Bondar AN, Elstner M, Entel P, Buss V. The retinal conformation and its environment in rhodopsin in light of a new 2.2 A crystal structure. J Mol Biol. 2004 Sep 10;342(2):571-83. PMID:[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15327956 15327956] doi:[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2004.07.044 10.1016/j.jmb.2004.07.044]</li> <li id="cite_note-Article3-11">↑ <sup>[[#cite_ref-Article3_11-0|12.0]]</sup> <sup>[[#cite_ref-Article3_11-1|12.1]]</sup> Janz JM, Farrens DL. Assessing structural elements that influence Schiff base stability: mutants E113Q and D190N destabilize rhodopsin through different mechanisms. Vision Res. 2003 Dec;43(28):2991-3002. PMID:[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14611935 14611935]</li> <li id="cite_note-Article19-12">↑ <sup>[[#cite_ref-Article19_12-0|13.0]]</sup> <sup>[[#cite_ref-Article19_12-1|13.1]]</sup> <sup>[[#cite_ref-Article19_12-2|13.2]]</sup> Kisselev OG. Focus on molecules: rhodopsin. Exp Eye Res. 2005 Oct;81(4):366-7. PMID:[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16051215 16051215] doi:[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.exer.2005.06.018 10.1016/j.exer.2005.06.018]</li> <li id="cite_note-Article2-13">↑ <sup>[[#cite_ref-Article2_13-0|14.0]]</sup> <sup>[[#cite_ref-Article2_13-1|14.1]]</sup> <sup>[[#cite_ref-Article2_13-2|14.2]]</sup> Verhoeven MA, Bovee-Geurts PH, de Groot HJ, Lugtenburg J, DeGrip WJ. Methyl substituents at the 11 or 12 position of retinal profoundly and differentially affect photochemistry and signalling activity of rhodopsin. J Mol Biol. 2006 Oct 13;363(1):98-113. Epub 2006 Jul 28. PMID:[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16962138 16962138] doi:[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2006.07.039 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.07.039]</li> <li id="cite_note-Article6-14">↑ <sup>[[#cite_ref-Article6_14-0|15.0]]</sup> <sup>[[#cite_ref-Article6_14-1|15.1]]</sup> <sup>[[#cite_ref-Article6_14-2|15.2]]</sup> <sup>[[#cite_ref-Article6_14-3|15.3]]</sup> Morris MB, Dastmalchi S, Church WB. Rhodopsin: structure, signal transduction and oligomerisation. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2009 Apr;41(4):721-4. Epub 2008 Aug 3. PMID:[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18692154 18692154] doi:[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2008.04.025 10.1016/j.biocel.2008.04.025]</li> <li id="cite_note-Textbook-15">↑ <sup>[[#cite_ref-Textbook_15-0|16.0]]</sup> <sup>[[#cite_ref-Textbook_15-1|16.1]]</sup> <sup>[[#cite_ref-Textbook_15-2|16.2]]</sup> <sup>[[#cite_ref-Textbook_15-3|16.3]]</sup> <sup>[[#cite_ref-Textbook_15-4|16.4]]</sup> Nelson, D., and Cox, M. Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry. 2008. 5th edition. W. H. Freeman and Company, New York, New York, USA. pp. 462-465.</li> <li id="cite_note-Article7-16">[[#cite_ref-Article7_16-0|↑]] Hurley JB, Spencer M, Niemi GA. Rhodopsin phosphorylation and its role in photoreceptor function. Vision Res. 1998 May;38(10):1341-52. PMID:[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9667002 9667002]</li> <li id="cite_note-ArticleOpsin2-17">↑ <sup>[[#cite_ref-ArticleOpsin2_17-0|18.0]]</sup> <sup>[[#cite_ref-ArticleOpsin2_17-1|18.1]]</sup> <sup>[[#cite_ref-ArticleOpsin2_17-2|18.2]]</sup> Park JH, Scheerer P, Hofmann KP, Choe HW, Ernst OP. Crystal structure of the ligand-free G-protein-coupled receptor opsin. Nature. 2008 Jul 10;454(7201):183-7. Epub 2008 Jun 18. PMID:[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18563085 18563085] doi:[http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature07063 10.1038/nature07063]</li>
<li id="cite_note-ArticleOpsin1-18">↑ <sup>[[#cite_ref-ArticleOpsin1_18-0|19.0]]</sup> <sup>[[#cite_ref-ArticleOpsin1_18-1|19.1]]</sup> Surya A, Knox BE. Enhancement of opsin activity by all-trans-retinal. Exp Eye Res. 1998 May;66(5):599-603. PMID:[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9628807 9628807] doi:[http://dx.doi.org/10.1006/exer.1997.0453 10.1006/exer.1997.0453]</li></ol></ref>
See Also
- Bacteriorhodopsin
- G protein-coupled receptors
- Membrane proteins
- Receptor
- Transmembrane (cell surface) receptors
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Wayne Decatur, Jaime Prilusky, Joel L. Sussman, Cinting Lim