Electrostatic potential maps
From Proteopedia
It is revealing to visualize the distribution of electrostatic charges, electrostatic potential, on molecular van der Waals surfaces. Most protein-protein and protein-ligand interactions are largely electrostatic in nature, via hydrogen bonds and ionic interactions. Their strengths are modulated by the nature of the solvent: pure water or high ionic strength aqueous solution[1].
Contents |
Gallery
| 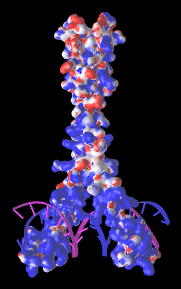
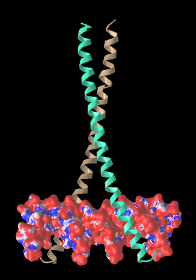
| Leucine zipper transcription regulator protein bound to DNA (5t01). The electrostatic potential maps show positively charged protein surface contacting negatively charged DNA.
Maps generated via FirstGlance in Jmol using iCn3D. |
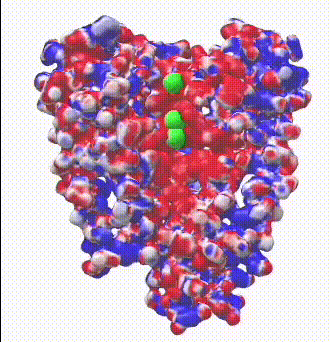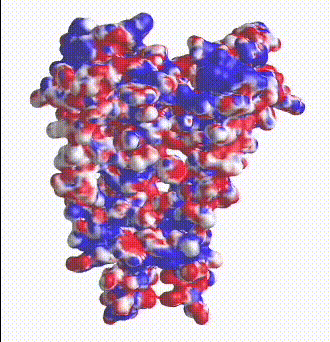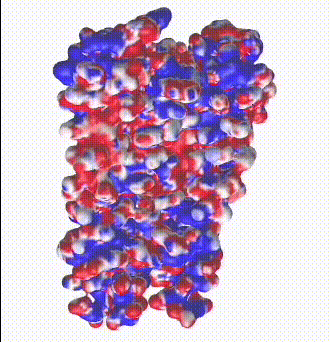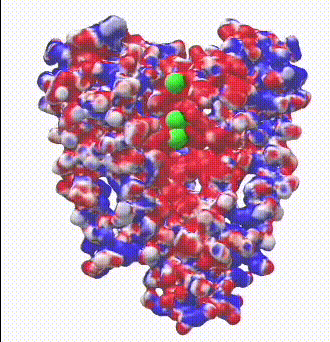
| Potassium channel (1bl8). The electrostatic potential map shows negatively charged protein surface lining the channel containing K+ ions.
Map generated by iCn3D after uploading a PDB file from which one of the 4 chains was removed to reveal the inside surface of the channel. |
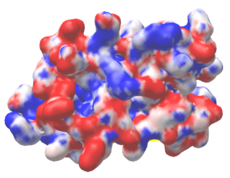
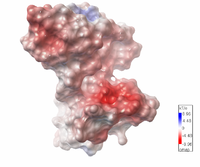
| Protein 1pgb is in the same orientation in all images. Positive + / Negative - | ||
|---|---|---|
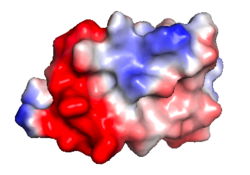
| 
| 
|
| Electrostatic potential map rendered by PyMOL using default molecular surface probe radius 1.4 Å. Method. | Electrostatic potential map rendered by iCn3D with "Potential contour" set to 4. Method. | Van der Waals model colored by charge with FirstGlance in Jmol. Sidechain nitrogens on Arg/Lys; oxygens on Asp/Glu. Method. |
| Electrostatic potential map of 1tsj made with the Embedded Python Molecular Viewer from the Center for Computational Structural Biology of the Scripps Research Institute.
Click on the image to enlarge. |
Methods
iCn3D
iCn3D via FirstGlance in Jmol
- Start FirstGlance in Jmol.
- Enter the desired PDB Id, such as 1ijw.
- Click the Views tab, then click Show More Views.
- Click Electrostatic Potential Map.
- Click Protein or DNA/RNA[2]. iCn3D will open in a new browser tab showing the electrostatic potential map.
- Optionally, in iCn3D, Menu: Style, Background, White.
- To spin, iCn3D Menu: View, Rotate, Auto Rotation.
In iCn3D
- Start the iCn3D web application.
- Enter the desired PDB Id, such as 1pgb, and click one of the Load buttons[2].
- Menu: Select, Defined Sets. In the list that appears, click on proteins (or optionally on nucleotices).
- Menu: Analysis, DelPhi Potential, DelPhi Potential. Click the Surface with Potential tab.
- Optional (to expand white regions), change Potential contour from 2 to 4.
- Click the button Surface with Potential.
- Menu (optional): Style, Background, White.
- To spin, Menu: View, Rotate, Auto Rotation.
To remove the yellow selection halo, enter the command (in the slot at the bottom) "select sets nothing".
PyMOL
PyMOL has a license fee, but is free for students and educators.
- Download and install PyMOL.
- Enter command "fetch 1pgb".
- Menu: All, Action, remove waters.
- Menu: 1pgb, Action, generate, vacuum electrostatics, protein contact potential (local).
- Enter command "bg_color white".
Optional: The probe radius used to generate the molecular surface can be changed, and the previously generated surface will immediately change. The command is "set solvent_radius, 1.2" (don't overlook the comma!).
Coloring Charged Atoms
- Start FirstGlance in Jmol.
- Enter the desired PDB Id, such as 1ijw.
- Click the Views tab, then click Charge...
See Also
- Electrostatic interactions in Proteopedia.
- Jmol/Electrostatic potential methods.
- Isopotential Map in Wikipedia
- Delphi Web Server
References
- ↑ This opening paragraph was adapted from text authored by User:Karsten Theis in Jmol/Electrostatic potential.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 To visualize the differences between the biological unit and asymmetric unit, view the PDB Id in http://firstglance.jmol.org, then click on Biological Unit 1.
