Introduction
COVID-19 was crazy! It achieves it's goal by the spike protein, on the surface of COVID-19, interacting with ACE2, angiotensin-converting enzyme, to allow entrance of the virus into the host cell [1].
Function
Mechanism
Active Site
In order to best target the RBD of the spike protein, the minibinders reveal a wide range of interactions to compete with .
The first design method, Rosetta, created AHB2 based on the single interacting helix of ACE2. With , we see two alpha helices mimicking ACE2. Hydrogen bonding interactions between N36, D11, K43, E41, and E30 of the minibinder interact with residues K417, R403, Y449, Q493, and N487, respectively, in the spike protein.
De novo designed proteins, as discussed previously, focused on computational design to determine residues best able to interact with the spike protein. We will focus on LCB1 and LCB3. reveals hydrogen bonding between D30 of the minibinder and both K417 and R403 of the spike protein, in addition to D17 and R14 of the minibinder interacting with Q493 of the spike protein. Similarly, reveals hydrogen bonding between D11 of the minibinder to K417 and R403 of the spike protein.
Within all four binding sites, we see two conserved residues throughout: K417 and Q493.
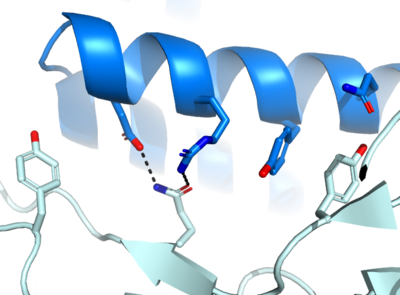
Figure 1. The coolest image of this protein's binding site EVAH!!!
References
[1]
[2]
[3]
[4]
[5]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Cao L, Goreshnik I, Coventry B, Case JB, Miller L, Kozodoy L, Chen RE, Carter L, Walls AC, Park YJ, Strauch EM, Stewart L, Diamond MS, Veesler D, Baker D. De novo design of picomolar SARS-CoV-2 miniprotein inhibitors. Science. 2020 Oct 23;370(6515):426-431. PMID:32907861 doi:10.1126/science.abd9909
- ↑ Wrapp D, Wang N, Corbett KS, Goldsmith JA, Hsieh CL, Abiona O, Graham BS, McLellan JS. Cryo-EM structure of the 2019-nCoV spike in the prefusion conformation. Science. 2020 Feb 19. pii: science.abb2507. doi: 10.1126/science.abb2507. PMID:32075877 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.abb2507
- ↑ Borkotoky S, Dey D, Hazarika Z. Interactions of angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 (ACE2) and SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain (RBD): a structural perspective. Mol Biol Rep. 2023 Mar;50(3):2713-2721. PMID:36562937 doi:10.1007/s11033-022-08193-4
- ↑ Zhang H, Lv P, Jiang J, Liu Y, Yan R, Shu S, Hu B, Xiao H, Cai K, Yuan S, Li Y. Advances in developing ACE2 derivatives against SARS-CoV-2. Lancet Microbe. 2023 May;4(5):e369-e378. PMID:36934742 doi:10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00011-3
- ↑ Zhu Y, Li M, Liu N, Wu T, Han X, Zhao G, He Y. Development of highly effective LCB1-based lipopeptides targeting the spike receptor-binding motif of SARS-CoV-2. Antiviral Res. 2023 Mar;211:105541. PMID:36682464 doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2023.105541
Student Contributors

