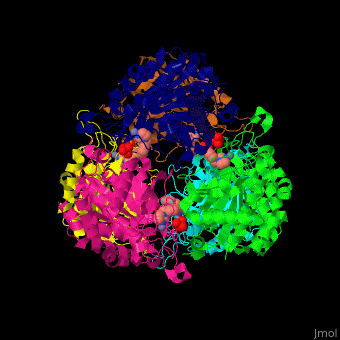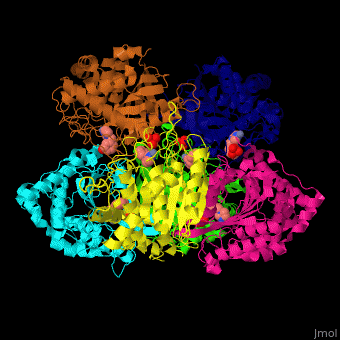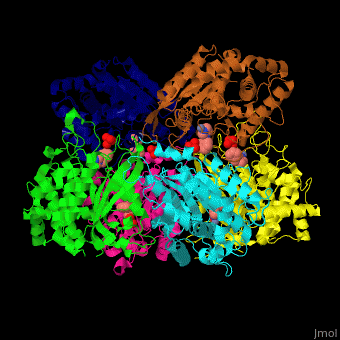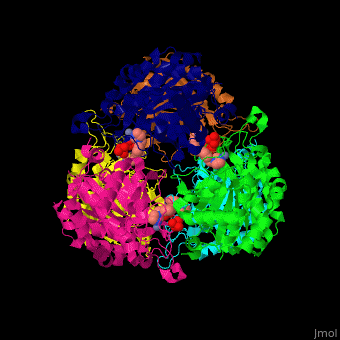
Function
Glutaminyl cyclase (QC) or glutaminyl-peptide cyclotransferase catalyzes the conversion of glutaminyl-peptide to 5-oxoprolyl-peptide and ammonia. Thus QC catalyzes the cyclization of an N-terminal glutamyl residue[1].
Relevance
The biological assembly of Human Glutaminyl cyclase is . QC is considered as a marker of thyroid tumors. QC acts on the generation of N-terminal pyroglutamyl groups of peptide hormones and amyloid-related plaque-forming peptides. The latter contributes to Alzheimer disease. Alzheimer patients show increased expression of QC[2] and QC inhibitors reduces the disease pathology and symptoms.
Structural highlights
The [3].