Cubic Diamond Lattice Metal-Organic Framework
From Proteopedia
| |||||||||||
Contents |
Significance
Since the proposal of this class of materials, metal-organic framework have been proven to support many roles. Applications to gas storage, analytical chemistry and (bio)sensors, batteries and fuel cell technology, separation science, synthesis and catalysis, harvesting of water from dry (low humidity) air, water purification and environmental remediation, capture/destruction of harmful agents, energy conversion and storage, hydrogen generation, food safety, and drug delivery & diagnostics/therapy have been demonstrated[2].
Highlighting the significance is the fact three chemists doing seminal work in this field were awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 2025. The structure featured here played a key role in establishing this field.
Technical Details
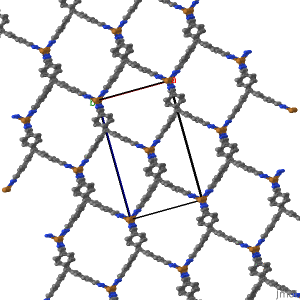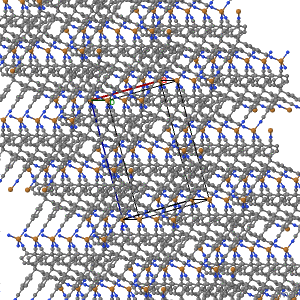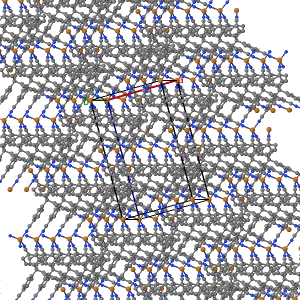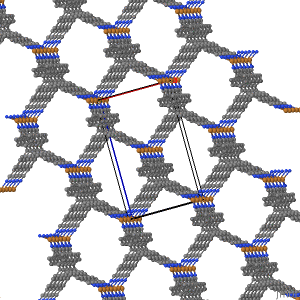
The views featuring the 1x1x3 set and the plane were built using the Jmol Crystal Symmetry Explorer to examine CSD Entry: JARMEU.
References
- ↑ B.F. Hoskins and R. Robson. 1989. Infinite polymeric frameworks consisting of three dimensionally linked rod-like segments. Journal of the American Chemical Society, v111, pg. 5962-5964, |DOI: 10.1021/ja00197a079
- ↑ https://www.nobelprize.org/uploads/2025/10/advanced-chemistryprize2025.pdf