4ald
From Proteopedia
|
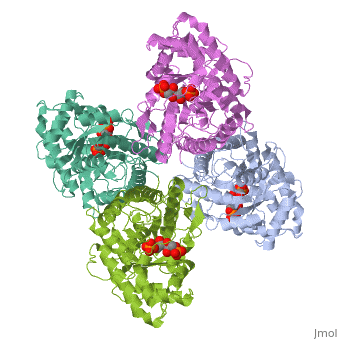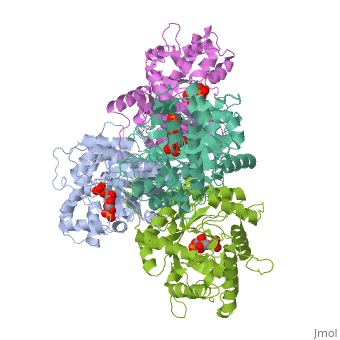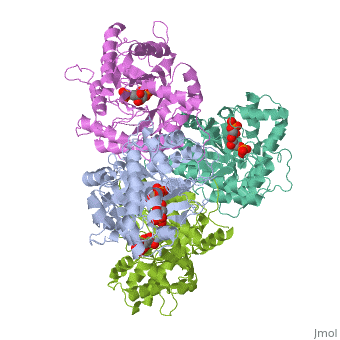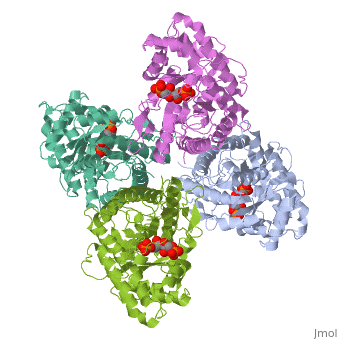
HUMAN MUSCLE FRUCTOSE 1,6-BISPHOSPHATE ALDOLASE COMPLEXED WITH FRUCTOSE 1,6-BISPHOSPHATE
Contents |
Overview
Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate aldolase catalyzes the reversible cleavage of, fructose 1,6-bisphosphate and fructose 1-phosphate to dihydroxyacetone, phosphate and either glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate or glyceraldehyde, respectively. Catalysis involves the formation of a Schiff's base, intermediate formed at the epsilon-amino group of Lys229. The existing, apo-enzyme structure was refined using the crystallographic free-R-factor, and maximum likelihood methods that have been shown to give improved, structural results that are less subject to model bias. Crystals were also, soaked with the natural substrate (fructose 1,6-bisphosphate), and the, crystal structure of this complex has been determined to 2.8 A. The apo, structure differs from the previous Brookhaven-deposited structure (1ald), in the flexible C-terminal region. This is also the region where the, native and complex structures exhibit differences. The conformational, changes between native and complex structure are not large, but the, observed complex does not involve the full formation of the Schiff's base, intermediate, and suggests a preliminary hydrogen-bonded Michaelis complex, before the formation of the covalent complex.
Disease
Known disease associated with this structure: Aldolase A deficiency OMIM:[103850]
About this Structure
4ALD is a Single protein structure of sequence from Homo sapiens with 2FP as ligand. The following page contains interesting information on the relation of 4ALD with [The Glycolytic Enzymes]. Active as Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase, with EC number 4.1.2.13 Structure known Active Site: SBL. Full crystallographic information is available from OCA.
Reference
Crystal structure of human muscle aldolase complexed with fructose 1,6-bisphosphate: mechanistic implications., Dalby A, Dauter Z, Littlechild JA, Protein Sci. 1999 Feb;8(2):291-7. PMID:10048322
Page seeded by OCA on Mon Nov 12 23:50:15 2007