This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Sandbox108
From Proteopedia
Glutamine synthetase assignment by UMBC undergraduate students
| |||||||||
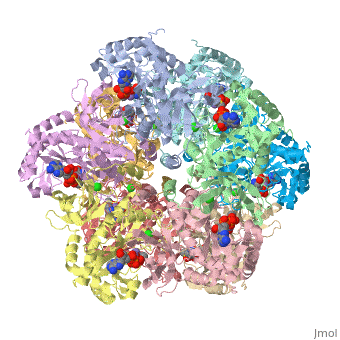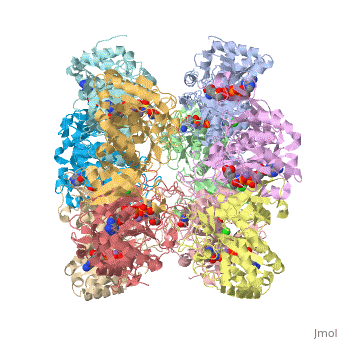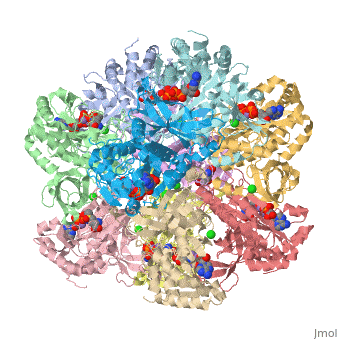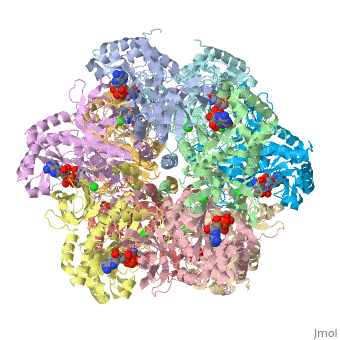
| 2qc8, resolution 2.60Å () | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligands: | , , , | ||||||||
| Gene: | GLUL, GLNS (Homo sapiens) | ||||||||
| Activity: | Glutamate--ammonia ligase, with EC number 6.3.1.2 | ||||||||
| Related: | 2ojw | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, RCSB, PDBsum | ||||||||
| Coordinates: | save as pdb, mmCIF, xml | ||||||||
OUTLINE
Tertiary Structure
Tertiary structure of protein is characterized by the “global” folding of a polypeptide chain [1] and has two domains in refined atomic model of glutamine synthetase from Salmonella typhimurium. Hydrophobic interaction is a major driving force determining the most tertiary structure of the proteins. [2] Hydrogen bonding <insert wiki showing the H.B> is crucial in stabilizing the tertiary structure as well. [3] Also, disulfide bonds <insert wiki showing the disulfide bonds of cysteine> between cysteine residues stabilize the tertiary structure. [4]
Glutamine synthetase from Salmonella has twenty three helix-helix interactions. [5] Hydrophobic/polar <hydrophobic/polar wiki> (put color) and hydrophilic <hydrophilic wiki>(put color) region of glutamine are combined together to fold proteins.
is within uncharged polar <insert wiki showing the uncharged polar groups>. Usually, uncharged polar groups are classified as hydrophilic <insert wiki showing the hydrophilic> that is found on the outside of proteins. Also, amino acids with the character of acidic or basic side chains are polar, showing on the outside of molecules <insert wiki showing the polar>. For glutamine, its side chain is uncharged and formed by replacing the hydroxyl of glutamic acid with an amine functional group. [6] In the other hand, glutamine has no side chain on non-polar group, however the side chain on non-polar groups of the proteins usually tends to be hydrophobic <insert wiki showing the hydrophobic of cysteine> and to cluster together on the inside.[7]