This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Sandbox 12
From Proteopedia
Green fluorescent protein (GFP), originally isolated from the jellyfish Aequorea victoria (PDB entry 1ema), fluorsceses green (509nm) when exposed to blue light (395nm and 475nm). It is one of the most important proteins used in biological research because it can be used to tag otherwise invisible gene products of interest and thus observe their existence, location and movement.
Exploring the Structure
|
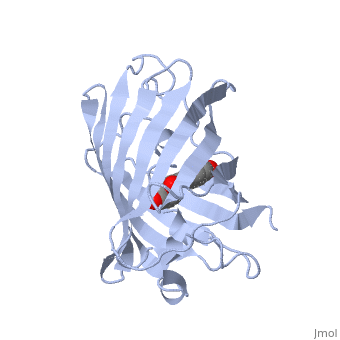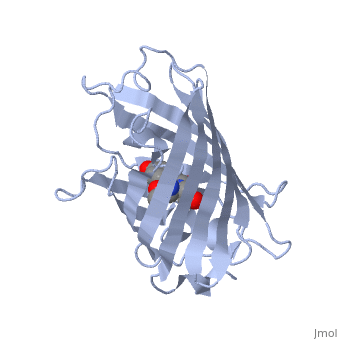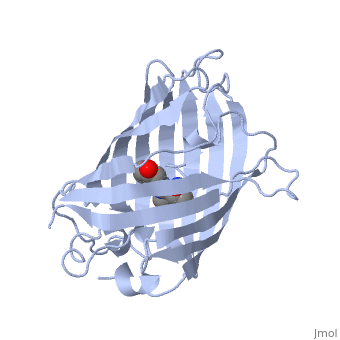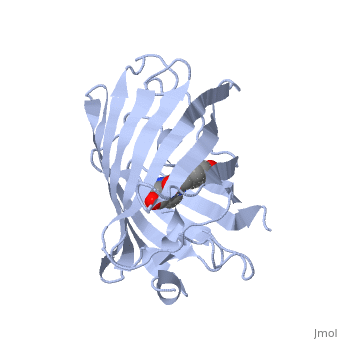
GFP is a beta barrel protein with 11 beta sheets. It is a 26.9kDa protein made up of 238 amino acids. The chromophore, responsible for the fluorescent properties of the protein, is buried inside the beta barrel as part of the central alpha helix passing through the barrel. The chromophore forms via spontaneous cyclization and oxidation of three residues in the central alpha helix: -Thr65 (or Ser65)-Tyr66-Gly67. This cyclization and oxidation creates the chromophore's five-membered ring via a new bond between the threonine and the glycine residues. [1]