This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
User:Burcu Baykal/Sandbox1
From Proteopedia
Hemostasis is a control mechanism in the circulatory system that responsible for the stoppage of bleeding by changing the fluid state of the blood into solid state. Hemostasis as two stages: primary homeostasis includes vascular contraction, platelet adhesion and formation of a soft aggregate plug. Primary Hemostasis starts very quickly after the injury. However it is temporary and local contraction that should be stabilized by the secondary hemostasis.
Secondary hemostasis is a complex system resulting fibrin formation as an output of the interaction between coagulation factors. Coagulation factors are serine proteases that forms coagulation cascade. It can be initiated via two different pathways: intrinsic and extrinsic.
Extrinsic cascade is activated upon a vascular damage by factor VII/VIIa and its membrane bound co-factor tissue factor(TF).The balance between hemostasis and thrombosis is very crucial that excessive cloth formation can be prevented by anticoagulants. Heparin-ATII is the most known anticoagulant that targets FXa and thrombi in the cascade. since the coagulation process starts with FVIIa-TF complex; it can be a very good therapeutic anticoagulant.
|
Factor VIIa
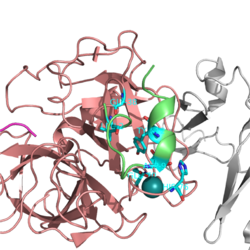
It is composed of 254-residue serine protease domain in the heavy chain and two EGF-like domains with a Gla domain in the light chain. Catalytic domain includes two six-stranded antiparallel β-barrels with the active-site cleft between them.N terminal Ile16 stabilizes active site forming salt bridge with Asp194.Catalytic Triad:Gly 193, Ser 195 and His 57.The amide nitrogen atoms of Gly 193 and Ser 195 form oxyanion hole. Oxyanion hole plays key role in stabilizing the negatively charged tetrahedral intermediate.<ref=1>
Inhibition of FVIIa-TF Complex
Human TF-FVIIa complex is inhibited by TFPI.It interacts with the catalytic triad at the active site either by reversible or irreversible. A new class of peptide inhibitors of FVIIa discvered using phage display that inhibites at the exosite on the TF-FVIIa complex.Polyvalent phage libraries searched and a `fully matured' consensus sequence; peptide E-76 (Ac-ALCDDPRVDRWYCQFVEG-NH2) was chosen for further characterization.The same dissociation constant found with FVIIa or TF±FVIIa by Surface plasmon resonance studies.No evidence for binding was detected for TF or thrombin, FXa,FIXa, FXIa, FXIIa, plasma kallikrein, activated protein C, tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA) and plasmin.Also,Binding to FVIIa was dependent on the presence of calcium.The figure shows the contact region of E-76 peptide inhibitor on FVIIa surface.<ref=2>
References
1.Crystal structures of uninhibited factor VIIa link its cofactor and substrate-assisted activation to specific interactions. J.Mol.Biol. 322: 591-603 2002
2.Peptide exosite inhibitors of factor VIIa as anticoagulants. Nature 404: 465-470 2000