2hym
From Proteopedia
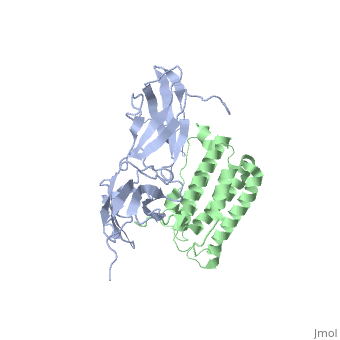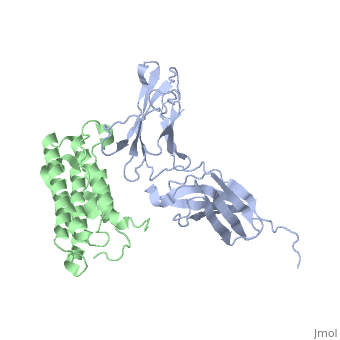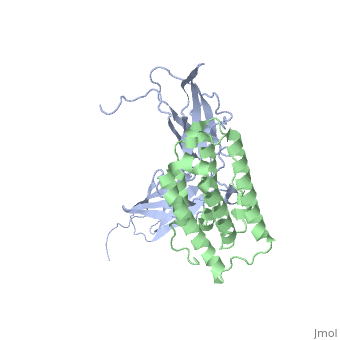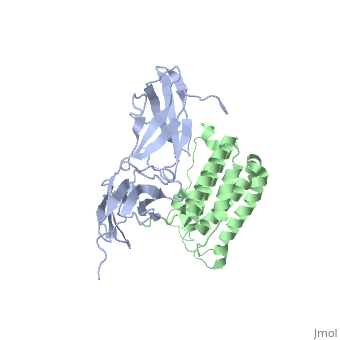
NMR based Docking Model of the Complex between the Human Type I Interferon Receptor and Human Interferon alpha-2
Structural highlights
Function[INAR2_HUMAN] Associates with IFNAR1 to form the type I interferon receptor. Receptor for interferons alpha and beta. Involved in IFN-mediated STAT1, STAT2 and STAT3 activation. Isoform 1 and isoform 2 are directly involved in signal transduction due to their association with the TYR kinase, JAK1. Isoform 3 is a potent inhibitor of type I IFN receptor activity.[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [IFNA2_HUMAN] Produced by macrophages, IFN-alpha have antiviral activities. Evolutionary ConservationCheck, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf. Publication Abstract from PubMedType I interferons (IFNs) are a family of homologous helical cytokines that exhibit pleiotropic effects on a wide variety of cell types, including antiviral activity and antibacterial, antiprozoal, immunomodulatory, and cell growth regulatory functions. Consequently, IFNs are the human proteins most widely used in the treatment of several kinds of cancer, hepatitis C, and multiple sclerosis. All type I IFNs bind to a cell surface receptor consisting of two subunits, IFNAR1 and IFNAR2, associating upon binding of interferon. The structure of the extracellular domain of IFNAR2 (R2-EC) was solved recently. Here we study the complex and the binding interface of IFNalpha2 with R2-EC using multidimensional NMR techniques. NMR shows that IFNalpha2 does not undergo significant structural changes upon binding to its receptor, suggesting a lock-and-key mechanism for binding. Cross saturation experiments were used to determine the receptor binding site upon IFNalpha2. The NMR data and previously published mutagenesis data were used to derive a docking model of the complex with an RMSD of 1 Angstrom, and its well-defined orientation between IFNalpha2 and R2-EC and the structural quality greatly improve upon previously suggested models. The relative ligand-receptor orientation is believed to be important for interferon signaling and possibly one of the parameters that distinguish the different IFN I subtypes. This structural information provides important insight into interferon signaling processes and may allow improvement in the development of therapeutically used IFNs and IFN-like molecules. Determination of the human type I interferon receptor binding site on human interferon-alpha2 by cross saturation and an NMR-based model of the complex.,Quadt-Akabayov SR, Chill JH, Levy R, Kessler N, Anglister J Protein Sci. 2006 Nov;15(11):2656-68. Epub 2006 Sep 25. PMID:17001036[6] From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine. See Also
References
| ||||||||||||||||||||