Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor
From Proteopedia
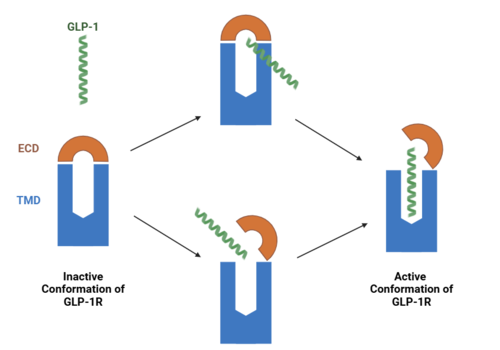
Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor (GLP-1R), is a Class-B G-Protein Coupled Receptor. GLP-1 acts on GLP-1R to lower blood glucose through glucose-dependent insulin, specifically as an incretin hormone.
Contents |
Function
GLP-1R mediates the action of glucagon-like peptides (GLP-1) which are hormones involved in nutrient intake, gastrointestinal motility, islet hormone secretion, cell proliferation and apoptpsis[1]. GLP-1R expression can be found in islet beta cells inside the pancreas. GLP-1 acts on GLP-1R to lower blood glucose through glucose-dependent insulin, specifically as an incretin hormone. To lower the risk of hypoglycemia, receptor agonists may stimulate the secretion of insulin, dependent on glucose. GLP-1R expression has also been detected in the brain, heart, kidney, stomach, and lungs along with indirectly promoting homeostasis in the liver, adipose tissue, and skeletal muscle. For example, signaling from the hypothalamus responds with decreased glucose uptake in skeletal muscle, though the receptor is not present.
Relevance
GLP-1R agonists are used in treatment of type 2 diabetes[2]. GLP-1 analogues can cross the brain-blood barrier and stimulate the GLP-1R in the brain. This stimulation is affecting mitochondrial functioning, protein aggregation, neuroinflammation, synaptic plasticity, learning and memory in models of Parkinson Disease and Alzheimer Disease[3]. It is a member of the glucagon receptor family of G protein-coupled receptors.
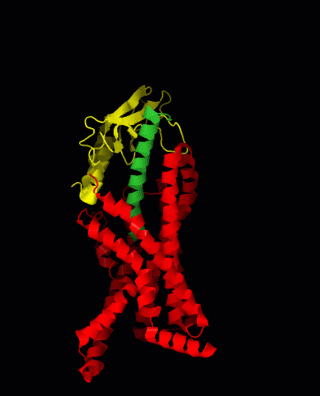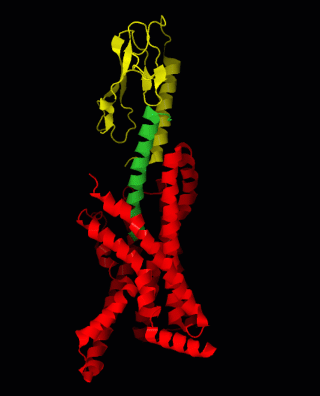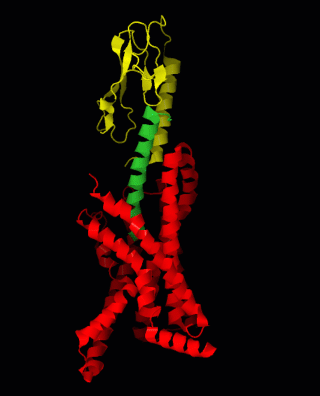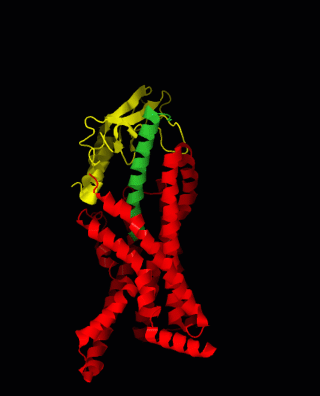
Structural highlights
| |||||||||||
See also:
3D structures of glucagon-like peptide receptor
Glucagon-like peptide receptor 3D structures
References
- ↑ Brubaker PL, Drucker DJ. Structure-function of the glucagon receptor family of G protein-coupled receptors: the glucagon, GIP, GLP-1, and GLP-2 receptors. Receptors Channels. 2002;8(3-4):179-88. PMID:12529935
- ↑ Donnelly D. The structure and function of the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor and its ligands. Br J Pharmacol. 2012 May;166(1):27-41. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01687.x. PMID:21950636 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01687.x
- ↑ Athauda D, Foltynie T. The glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP) receptor as a therapeutic target in Parkinson's disease: mechanisms of action. Drug Discov Today. 2016 May;21(5):802-18. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2016.01.013. Epub, 2016 Feb 3. PMID:26851597 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.drudis.2016.01.013
- ↑ doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-6438-9_101967-1
- ↑ Underwood CR, Garibay P, Knudsen LB, Hastrup S, Peters GH, Rudolph R, Reedtz-Runge S. Crystal structure of glucagon-like peptide-1 in complex with the extracellular domain of the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor. J Biol Chem. 2010 Jan 1;285(1):723-30. Epub 2009 Oct 27. PMID:19861722 doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.033829
- ↑ Xiao Q, Jeng W, Wheeler MB. Characterization of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor-binding determinants. J Mol Endocrinol. 2000 Dec;25(3):321-35. PMID:11116211 doi:10.1677/jme.0.0250321
- ↑ Wu F, Yang L, Hang K, Laursen M, Wu L, Han GW, Ren Q, Roed NK, Lin G, Hanson MA, Jiang H, Wang MW, Reedtz-Runge S, Song G, Stevens RC. Full-length human GLP-1 receptor structure without orthosteric ligands. Nat Commun. 2020 Mar 9;11(1):1272. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-14934-5. PMID:32152292 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-14934-5
Student contributors
This page was updated as a two-week project of an undergraduate biochemistry course. Karsten Theis would like to acknowledge contributors Ahmad Al Zubaidi, Benjamin Gordon, Andrew and Jordyn.