Crystal structures of glutamyl-tRNA synthetase from Elizabethkingia anopheles and E. meningosepticum
Lauryn Brooks, Sandhya Subramanian, David M. Dranow, Stephen J. Mayclin, Peter J. Myler, and Oluwatoyin A. Asojo [1]
Molecular Tour
Elizabethkingia bacteria are emerging pathogens globally that cause opportunistic and nosocomial infections with up to 40% mortality among the immune-compromised. Elizabethkingia species are in the pipeline of organisms for high throughput structural analysis at the Seattle Structural Genomics Center for Infectious Disease (SSGCID). These efforts include the structure-function analysis of potential therapeutic targets. Glutamyl-tRNA synthetase (GluRS) is essential to the tRNA aminoacylation and is investigated as a bacterial drug target. The SSGCID produced crystallized and determined high-resolution structures of GluRS from Elizabethkingia meningosepticum (EmGluRS; 6brl) and Elizabethkingia anopheles (EaGluRS; 6b1z). EmGluRS was co-crystallized with glutamate, while EaGluRS is an apo-structure.
has a HUP-domain (orange), a Zn-binding-domain (green), and an anticodon binding domain (blue). The HUP domain and Zn-binding domain make up the N-terminal tRNA synthetases binding domain that binds the glutamate (spheres).
. Mg2+ ion from EaGluRS is shown as a green sphere, glutamate molecule shown as spheres (colored by atoms with white, carbons, red, oxygen, and blue nitrogen spheres), formate and ethylene glycol from crystallization are shown as sticks (atoms colored in CPK).
EmGluRS shares ~97% sequence identity with EaGluRS but less than 39% sequence identity with any other structures in the Protein Data Bank. EmGluRS and EaGluRS have prototypical bacterial GluRS topology. EmGluRS and EaGluRS have similar binding sites and tertiary structures to other bacterial GluRS that are promising drug targets. These structural similarities can be exploited for drug discovery.
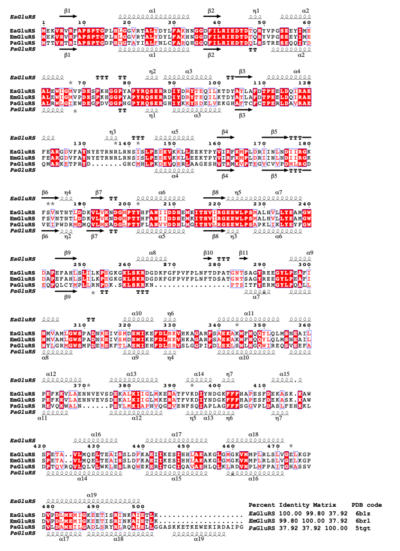
Structural and primary sequence alignment of EaGluRS, EmGluRS, and PaGluRS. The secondary structure elements are as follows: α- helices are shown as large coils, 310 helices are shown in small coils labeled η, beta-strand are shown in arrows labeled β, and beta-turns are labeled TT. The identical residues are shown on a red background with conserved residues in red and conserved regions in blue boxes.
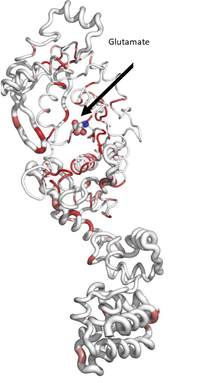
Ribbon diagram calculated by ENDScript. Circumference of the ribbon (sausage) represents relative structural conservation compared to other GluRS structures. Thinner ribbons represent higher conserved regions, while thicker ribbons represent lower conserved regions.
colored by sequence conservation with red indicating identical residues. Atoms of glutamate are colored in CPK.
of PaGluRS (pdb entry 5tgt, yellow), EmGluRS (gray), and EaGluRS (cyan).
References
- ↑ Brooks L, Subramanian S, Dranow DM, Mayclin SJ, Myler PJ, Asojo OA. Crystal structures of glutamyl-tRNA synthetase from Elizabethkingia anopheles and E. meningosepticum. Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2022 Aug 1;78(Pt 8):306-312. doi:, 10.1107/S2053230X22007555. Epub 2022 Jul 28. PMID:35924598 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1107/S2053230X22007555



