| Flexible regions govern promiscuous binding of IL-24 to receptors IL-20R1 and IL-22R1
Jiří Zahradník, Lucie Kolářová, Yoav Peleg, Petr Kolenko, Silvie Svidenská, Tatsiana Charnavets, Tamar Unger, Joel L. Sussman, and Bohdan Schneider [1]
Molecular Tour
Interleukin 24 (IL-24) is cytokine, member of Interleukin 10 family. It forms an IL-20 subfamily with IL-19, IL-20, IL-22 because all these interleukins use the common class II cytokine receptor subunits and have similarities in biological functions [2]. IL-24 signals via two heterodimeric receptor complexes IL-22R1/IL-20R2 and IL-20R1/IL-20R2 and activates the STAT3 and STAT1 signaling [3][4] (see static image and 3D scenes below).
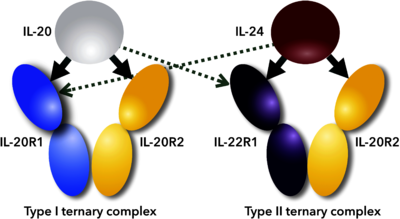 Scheme of promiscuous binding of IL-20 and IL-24 to signaling receptors IL-20R1 and IL-22R1. Arrows indicate binding between cytokines and their receptors; thick arrows show preferential binding, dashed ones alternative binding to the promiscuous receptors. [5]IL-24 is associated with multiple diseases, including the promotion and amplification of inflammatory responses during autoimmune and chronic inflammation [2], psoriasis-like skin inflammation [8], epidermal inflammation induced by stresses [9], inflammatory bowel disease [10][11], and also with host defense during bacterial infection [12]. Some studies suggest anti-cancer activities that increased the interest in this molecule.
One of the stable variants (IL-24B) was crystallized, its structure solved at 1.3 Å resolution and deposited to PDB under the code 6gg1. This structure together with the recently published crystal structure of the ternary complex of IL-24 fused to IL-22R1 and co-expressed with IL-20R2 (PDB ID 6df3[7]) allowed us to analyze the role of the mutated amino acid residues protein stability, flexibility, and binding to the cognate receptors. . Based on the analysis, we expressed a series of variants back engineered from the PROSS designed variant by changing the critical residues back to their wild types. We revealed that re-introduction of a single IL-24 wild type residue (T198) to the patch interacting with receptors 1 restored 80 % of the binding affinity and signaling capacity accompanied by an acceptable drop in the protein stability by 9°C.
Additional reading: [13][14][15][16]
PDB reference: Structure of PROSS-edited human interleukin 24, 6gg1.
References
- ↑ Zahradnik J, Kolarova L, Peleg Y, Kolenko P, Svidenska S, Charnavets T, Unger T, Sussman JL, Schneider B. Flexible regions govern promiscuous binding of IL-24 to receptors IL-20R1 and IL-22R1. FEBS J. 2019 Jun 1. doi: 10.1111/febs.14945. PMID:31152679 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/febs.14945
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Rutz S, Wang X, Ouyang W. The IL-20 subfamily of cytokines--from host defence to tissue homeostasis. Nat Rev Immunol. 2014 Dec;14(12):783-95. doi: 10.1038/nri3766. PMID:25421700 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nri3766
- ↑ Dumoutier L, Leemans C, Lejeune D, Kotenko SV, Renauld JC. Cutting edge: STAT activation by IL-19, IL-20 and mda-7 through IL-20 receptor complexes of two types. J Immunol. 2001 Oct 1;167(7):3545-9. PMID:11564763
- ↑ Wang M, Liang P. Interleukin-24 and its receptors. Immunology. 2005 Feb;114(2):166-70. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2005.02094.x. PMID:15667561 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2567.2005.02094.x
- ↑ Akdis M, Burgler S, Crameri R, Eiwegger T, Fujita H, Gomez E, Klunker S, Meyer N, O'Mahony L, Palomares O, Rhyner C, Ouaked N, Schaffartzik A, Van De Veen W, Zeller S, Zimmermann M, Akdis CA. Interleukins, from 1 to 37, and interferon-gamma: receptors, functions, and roles in diseases. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011 Mar;127(3):701-21.e1-70. doi:, 10.1016/j.jaci.2010.11.050. PMID:21377040 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2010.11.050
- ↑ Logsdon NJ, Deshpande A, Harris BD, Rajashankar KR, Walter MR. Structural basis for receptor sharing and activation by interleukin-20 receptor-2 (IL-20R2) binding cytokines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Jul 31;109(31):12704-9. Epub 2012 Jul 16. PMID:22802649 doi:10.1073/pnas.1117551109
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Lubkowski J, Sonmez C, Smirnov SV, Anishkin A, Kotenko SV, Wlodawer A. Crystal Structure of the Labile Complex of IL-24 with the Extracellular Domains of IL-22R1 and IL-20R2. J Immunol. 2018 Aug 15. pii: jimmunol.1800726. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1800726. PMID:30111632 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1800726
- ↑ Kumari S, Bonnet MC, Ulvmar MH, Wolk K, Karagianni N, Witte E, Uthoff-Hachenberg C, Renauld JC, Kollias G, Toftgard R, Sabat R, Pasparakis M, Haase I. Tumor necrosis factor receptor signaling in keratinocytes triggers interleukin-24-dependent psoriasis-like skin inflammation in mice. Immunity. 2013 Nov 14;39(5):899-911. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2013.10.009. Epub 2013, Nov 7. PMID:24211183 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2013.10.009
- ↑ Jin SH, Choi D, Chun YJ, Noh M. Keratinocyte-derived IL-24 plays a role in the positive feedback regulation of epidermal inflammation in response to environmental and endogenous toxic stressors. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2014 Oct 15;280(2):199-206. doi:, 10.1016/j.taap.2014.08.019. Epub 2014 Aug 27. PMID:25168428 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2014.08.019
- ↑ Andoh A, Shioya M, Nishida A, Bamba S, Tsujikawa T, Kim-Mitsuyama S, Fujiyama Y. Expression of IL-24, an activator of the JAK1/STAT3/SOCS3 cascade, is enhanced in inflammatory bowel disease. J Immunol. 2009 Jul 1;183(1):687-95. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0804169. Epub 2009 Jun, 17. PMID:19535621 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.0804169
- ↑ Fonseca-Camarillo G, Furuzawa-Carballeda J, Granados J, Yamamoto-Furusho JK. Expression of interleukin (IL)-19 and IL-24 in inflammatory bowel disease patients: a cross-sectional study. Clin Exp Immunol. 2014 Jul;177(1):64-75. doi: 10.1111/cei.12285. PMID:24527982 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/cei.12285
- ↑ Ma Y, Chen H, Wang Q, Luo F, Yan J, Zhang XL. IL-24 protects against Salmonella typhimurium infection by stimulating early neutrophil Th1 cytokine production, which in turn activates CD8+ T cells. Eur J Immunol. 2009 Dec;39(12):3357-68. doi: 10.1002/eji.200939678. PMID:19830736 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/eji.200939678
- ↑ Goldenzweig A, Goldsmith M, Hill SE, Gertman O, Laurino P, Ashani Y, Dym O, Unger T, Albeck S, Prilusky J, Lieberman RL, Aharoni A, Silman I, Sussman JL, Tawfik DS, Fleishman SJ. Automated Structure- and Sequence-Based Design of Proteins for High Bacterial Expression and Stability. Mol Cell. 2016 Jul 21;63(2):337-346. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.06.012. Epub 2016, Jul 14. PMID:27425410 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2016.06.012
- ↑ Musil M, Stourac J, Bendl J, Brezovsky J, Prokop Z, Zendulka J, Martinek T, Bednar D, Damborsky J. FireProt: web server for automated design of thermostable proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Jul 3;45(W1):W393-W399. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx285. PMID:28449074 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx285
- ↑ Frey S, Gorlich D. A new set of highly efficient, tag-cleaving proteases for purifying recombinant proteins. J Chromatogr A. 2014 Apr 11;1337:95-105. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2014.02.029. Epub , 2014 Feb 19. PMID:24636565 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2014.02.029
- ↑ Frey S, Gorlich D. Purification of protein complexes of defined subunit stoichiometry using a set of orthogonal, tag-cleaving proteases. J Chromatogr A. 2014 Apr 11;1337:106-15. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2014.02.030. Epub , 2014 Feb 19. PMID:24636567 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2014.02.030
|


