Structural Characterization of Metal Binding to a Cold-adapted Frataxin
Martín E. Noguera, Ernesto A. Roman, Juan B. Rigal, Alexandra Cousido-Siah, André
Mitschler, Alberto Podjarny, and Javier Santos [1]
Molecular Tour
Iron is an essential metal for organisms, with a remarkable ability to cycle between reduced and oxidized states. This property renders it very helpful in biosynthetic and energy-obtaining processes, but simultaneously entails potential toxic effects resulting from oxidative damage to biomolecules. is an evolutionary conserved protein involved in iron metabolism, which exact function is unknown, but available evidence suggest that FXN is a regulator of Fe-S cluster assembly and/or an iron chaperone. Deficiency in FXN's expression causes Friedreich's Ataxia, a neuro and cardio-degenerative disease. Therefore, it is of major interest to characterize the molecular details of iron binding by FXN, and the effects of this interaction in FXN's structure. In this work, we carried out a structural characterization of metal interaction to a cold-adapted frataxin (from a psychrophilic bacterium). We used (4lk8) and (4lp1) as metal mimetics of iron in reduced or oxidized states. We identified a number of binding sites, several of them are novel as compared with previous studies in mesophile variants of FXN.
- Localization of Co ions associated with FXN: ; ; .
- Localization of Eu ions associated with FXN: ; ; ; .
Metal ions are represented as spheres, along with the side chains involved in metal coordination (using a distance cutoff of 3 Å). Protein chains are shown as ribbon models.
The metals locate mainly in a region of high density of negative charge, the so-called "", which is also the surface of interaction with the Fe-S cluster assembly machinery. No major changes occurs in FXN structures upon interaction with metals, when derivative structures are compared with the previously determined apo form (PDB ID: 4hs5), but subtle changes in crystallographic B-factors occur in two regions of the protein not in direct contact with metals. This changes suggest localized changes in internal motions, with potential impact in interaction with partner proteins (see the static images below).
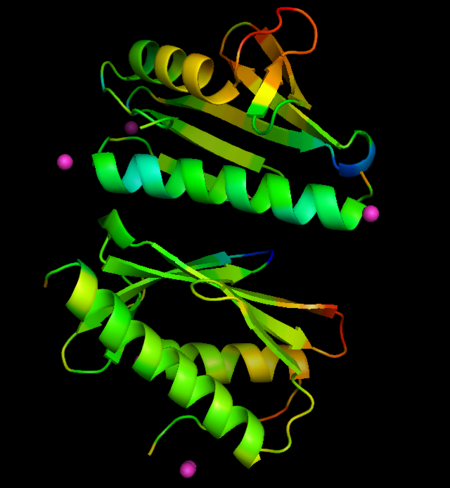
Changes in B-factors mapped onto the structure, color ranges from blue (decreased value) to red (increased value). Co derivative
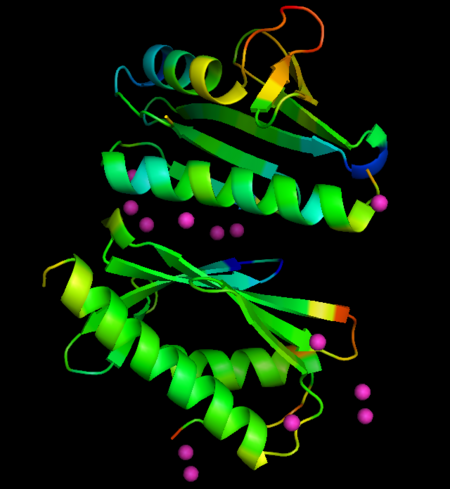
Changes in B-factors mapped onto the structure, color ranges from blue (decreased value) to red (increased value). Eu derivative
PDB references: Crystal structure of CyaY protein from Psychromonas ingrahamii in complex with Co(II), 4lk8; Crystal structure of CyaY protein from Psychromonas ingrahamii in complex with Eu(III), 4lp1.



