PARTIALLY DEGLYCOSYLATED GLUCOCERAMIDASE
(see also Treatment of Gaucher disease)
Publication Abstract from PubMed
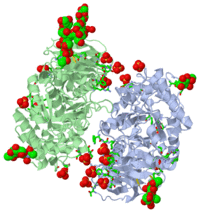
Gaucher disease is caused by mutations in the gene encoding acid-beta-glucosidase. A recombinant form of this enzyme, Cerezyme, is used to treat Gaucher disease patients by ;enzyme-replacement therapy'. Crystals of Cerezyme after its partial deglycosylation were obtained earlier and the structure was solved to 2.0 A resolution [Dvir et al. (2003), EMBO Rep. 4, 704-709]. The crystal structure of unmodified Cerezyme is now reported, in which a substantial number of sugar residues bound to three asparagines via N-glycosylation could be visualized. The structure of intact fully glycosylated Cerezyme is virtually identical to that of the partially deglycosylated enzyme. However, the three loops at the entrance to the active site, which were previously observed in alternative conformations, display additional variability in their structures. Comparison of the structure of acid-beta-glucosidase with that of xylanase, a bacterial enzyme from a closely related protein family, demonstrates a close correspondence between the active-site residues of the two enzymes.
Structural comparison of differently glycosylated forms of acid-beta-glucosidase, the defective enzyme in Gaucher disease., Brumshtein B, Wormald MR, Silman I, Futerman AH, Sussman JL, Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2006 Dec;62(Pt 12):1458-65. Epub 2006, Nov 23. PMID:17139081
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.
The of the crystal structure of velaglucerase alfa (colored red) (2wkl) reveals that it is very similar to those of the recombinant GlcCerase produced in Chinese hamster ovary cells (imiglucerase, Cerezyme®, colored blueviolet, 2j25) and in transgenic carrot cells (prGCD, 2v3f). of the two individual molecules in the asymmetric unit of velaglucerase alfa and imiglucerase demonstrates striking similarity between positions of catalytic residues E235 and E340 (colored orange) in all 4 molecules. The position of H311 is also very similar in all 4 molecules, whereas the conformations of 3 other active site residues W312, Y313, and, especially N396 are somewhat different. The active site residues (except E235 and E340) of the two individual molecules in the asymmetric unit of velaglucerase alfa are colored: subunit A (red), subunit B (lime) and of imiglucerase: subunit A (blueviolet), subunit B (magenta). Imiglucerase and pr-GlcCerase contain a at residue 495 (blueviolet), whereas velaglucerase alfa contains (red). Mutations which cause Gaucher disease, are close to R495 near the N-terminus of GlcCerase. The (its glycans are colored blue) and (its glycans are colored magenta) have different carbohydrate composition.
About this Structure
2J25 is a [Single protein] structure of acid-beta-glucosidase from [Homo sapiens] with NAG and SO4 as [ligands]. Active as [Glucosylceramidase], with EC number [3.2.1.45]. Structure known Active Site: AC1. Full crystallographic information is available from [OCA].
3D structure of β-glucosidase
Beta-glucosidase