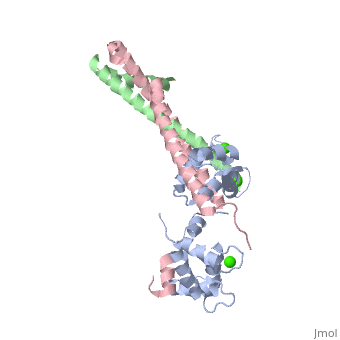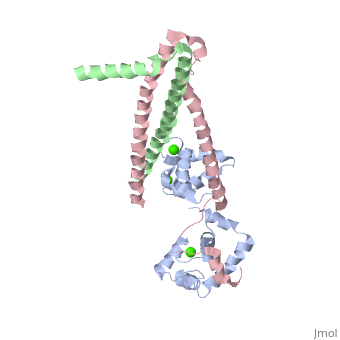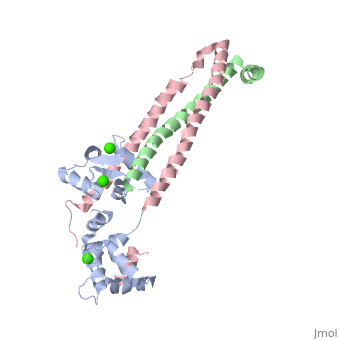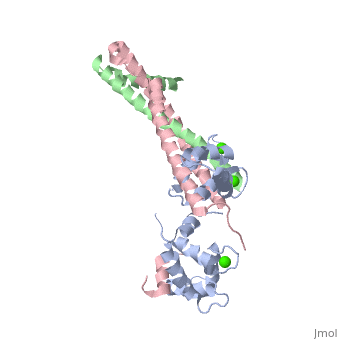
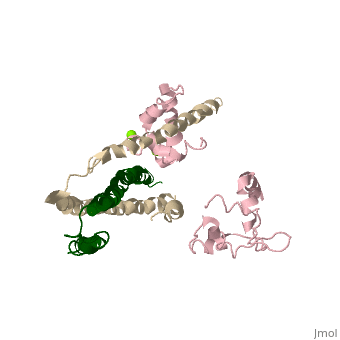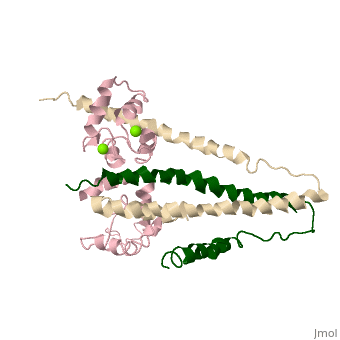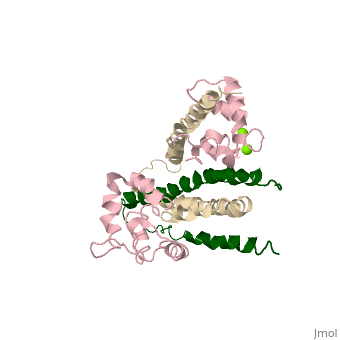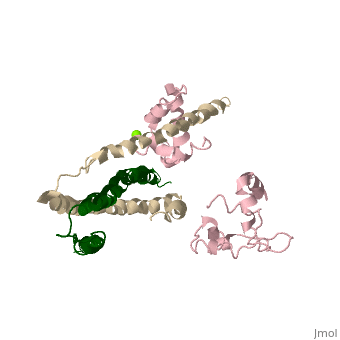
3 Subunits shown
1) TroponinT in yellow shown
Amino acids 159-248; Maia et al found no visible electron density @249-262
Cleavage with Chymotrypsin gives two fragments:
> TnT1 (1-155) Interacts with Tropomyosin (Truncated from this crystal structure)
> TnT2 (156-262) required for Troponin assembly, also interacts with Tropomyosin, shown
2) TroponinI in Cyan shown
Amino acids 3-143; no visible electron density for amino acids 144-182 (see section below)
> Inhibitory Segment (amino acids 104-115), binds actin in the absence of Ca2+. Shown in dark blue
> Second Actin binding site ( amino acids 140-148), shown in dark blue.
> Switch Segment, aka transducer (amino acids 116-131) shown ; binds Calcium activated
TnC's N-Terminus in exposed hydrophobic cavity.
3) TroponinC in Red shown
> Four EF-Hands
> Single a-helix linker connects N-Terminal regulatory (Two metal binding sites that prefer Calcium) and C-Terminal
structural lobes (Two metal binding sites that can bind other metals including Mg2+ or Ca2+).
Interactions
> Long helices of TnI (58-102; Cyan) and TnT2 (200-245; Yellow) = coiled coil;
> (8-48) + IT coiled coil, shown = hold TnC C-Terminal domain
> A-Helix linker defines dumbbell shape, approximately perpendicular to IT coil
> TnC metal binding sites 1&2 (N-terminal domain) + 3&4 (C-Terminal Domain) are occupied by calcium
> TnC helices B&C are in open confirmation
> TnI switch segment is bound in between the EF-Hands helices.
> TnI switch segment "registered" via TnC Glu-63 Gln-84 and TnI Arg-115 on pocket exterior
> TnI inhibitory segment is an ordered loop that interacts with TnI via hydrophobic interactions, and interacts with TnC via
electrostatic interactions only in Ca2+ activated
> TnI 113-115 = unlike in cardiac uniquely ordered, lay along TnC central helix
> TnI 132-143 = loop that binds N-terminal lobe of TnC
> 144-182 = Disordered, and assumed to bind actin
Dumbbell shaped
> Alpha helix linker segment connects regulatory and structural lobe.
> N-terminus regulatory lobe has 2 metal binding sites (1 and 2) that prefer Ca2+.
More precisely
> C-terminus structural lobe has 2 metal binding sites (3 and 4) that bind Mg2+ in a relaxed muscle, and Ca2+ in active muscle.
104 - 115 = inhibitory segment
140 - 148 = 2nd actin binding site
116 - 131 = "Switch Segment" binds