Overview
3CBW exists as a homodimeric quaternary structure. Analyzing primary and quaternary structures of 3CBW with SPRITE and Chimera revealed two chains identical in both shape and sequence. Each chain is a little over 300 residues long, and the entire complex has a molecular weight of approximately 80.65 kDa.
3CBW proteins originate from bacterial species Bacillus Subtilis (B.S.). InterPro search results show how nearly every enzyme with similar sequencing to 3CBW is found in various bacteria. Additionally, the PDB entry for 3CBW notes how it potentially can be found in B.S., the best studied gram-positive bacterial species which has probiotic properties.
Family and Superfamily
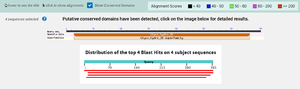
Research suggests that 3CBW is a member of the Glycoside Hydrolase super family which was found using BLAST. This means that the protein possibly has the ability to hydrolyze glycosidic bonds between two or more carbohydrates. Additionally, 3CBW is also recognized under the beta-mannanase family. This was confirmed with InterPro which showed 3CBW being highly conserved with this family, having over 300 shared amino acids.
Using Dali, it was found that 3CBW was similar in structure and sequence to proteins 2QHA (Beta-1,4-mannanase) and 2WHK (Mannan endo-1,4-beta-mannosidase) which come from the bacterial species Bacillus Subtilis. Furthermore, BLAST confirmed that 3CBW is similar to the enzymes that come from this bacterial species in terms of functionality.
Through a search on InterPro, it was determined that 3CBW has a glycosyl hydrolase family 26 domain. This domain consists mostly of endo-beta-1,4-mannanases and typically has a beta/alpha 8-barrel folding motif. Proteins in this domain also tend to have two Glu residues located respectfully on strands beta-4 and beta-7 that act as the catalytic acid/base and nucleophile in a double-displacement mechanism.
Sequence Analysis
According to BLAST, 3CBW has similar sequences to 2QHA (Beta-1,4-mannanase) and 2WHK (Mannan endo-1,4-beta-mannosidase). This means that 3CBW is in the mannanase super family.
Structural Analysis
Using Right-hand SPRITE analysis, it showed that 3BCW had similar residues to small amino acid chains. Specific residues are Ala. 76, Ile. 79, Gly. 61, Val. 293, the first two being on the A chain side and the second being on the B chain side of the 3CBW. Comparing 3CBW to 1BHG, which is human beta-glucuronidase, the RMSD value was a difference of 0.46 angstroms.
With the use of DALI, it was determined that 3CBW is most similar to Beta-1,4-Mannanase and Mannan Endo-1,4-Beta-Mannosidase. Both of these enzymes hydrolyzes different linkages.
Substrates
Using SwissDock, it was determined that larger, cyclic molecules are good substrates that would have the best binding affinity to 3CBW, each had about a -7 kcal/mol binding affinity. These large molecules are 4-Nitrophenyl N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminide, 4-Nitrophenyl α-D-glucopyranoside, and p-nitrophenyl phosphate.
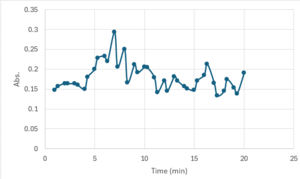
Bradford Assay Results
3CBW is catalytically active at a higher temperature (70 ºC) when reacted with p-nitrophenol(PNP).
Theoretical Functionality and Proposed Bodily Purpose
According to our research, 3CBW is a glycoside hydrolase whose job is to hydrolyze glycosidic bonds between two or more carbohydrates. Since this protein was found to most likely come from the bacterial species Bacillus Subtilis, it is highly likely that this protein was found in the human gastrointestinal tract. That is because Bacillus Subtilis is a probiotic bacteria and can aid in digestion and support a healthy microbiome.
This bacterial species offers several potential gut and immune health benefits, and it can be sourced through probiotic supplements or by eating fermented foods. In consuming such things, a person can increase the amount of this bacteria in their gastrointestinal tract and therefore aid in the body's ability to break down food.
Substrates: 4-Nitrophenyl N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminide, 4-Nitrophenyl α-D-glucopyranoside, and P-Nitrophenyl Phosphate
Binding sites: Glu. 100, Thr. 101, Ile. 104, Glu. 105