AcrA is a Multidrug efflux system protein. It belongs to resistance nodulation cell division (RND) family protein, which utilize electrochemical gradient to energize efflux of antibiotics and other compounds out of the bacterial cells [1]. RND system consists of large complexes of three essential proteins and work together as a multiprotein efflux system. Two most studied RND systems are Escherichia coli AcrA-AcrB-TolC and Pseudomonas aeruginosa MexA-MexB-OprM, which are known to efflux antibiotics, heavy metals, dyes, detergents, solvents, plus many other substrates [2].
Stable core of AcrA
Four molecules of AcrA (45-312 residues) in asymmetric unit of the crystal pack as an apparent . Each monomers are labeled as A (in cyan), B (in orange), C (in green) and D (in yellow). A, B / C, D are related to one another by approximate . Each set of dimers are related to one another by approximate [3].
Each is a sickle shaped molecule comprising three domains viz. , , and coiled coil . β-barrel domain comprises six anti-parallel β-sheets and a short α-helix. Lipoyl domain is present in the central part of the AcrA monomer made up of interrupted by an α-helical hairpin. Each half of the lipoyl motif is homologous to each other and consist of four β-strands in the form of a β-sandwich. The coiled coil domain consists of five heptad repeats per helix. Two α-helices are packed together as a canonical knobs-into-holes by hydrophobic side chains in the of the heptad repeats [4] [5]. Crystal structure provide evidence for the flexibility of the hinge region between α-helical hairpin and lipoyl domain. The difference in hinge angle in case of B and C chain varies approximately by 15° overall and 21 Å at the loop located at the top of the hairpin.
Assembly within biological system
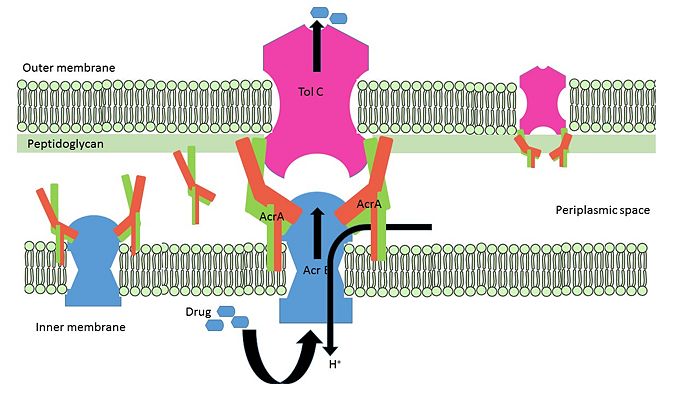
Schematic representation of free AcrA; bipartite complex between AcrA-AcrB, AcrA-TolC; Tripartite complex between AcrAB-TolC.Figure modified from Qiang Ge et al, 2009
. AcrA is present within
E. coli cells as a part of tripartite membrane associated efflux system along with
AcrB and
TolC. AcrA is present in the periplasmic space of cell with the proton antiporter AcrB in the inner-membrane and channel TolC in the outer membrane. It can it can remain free or form bipartite complexes with AcrB and TolC. The lipoyl and β-barrel domain of AcrA interact with AcrB, whereas the α-helical hairpin domain interact with TolC
[6].
ArcA remains attached to the inner membrane via lipid acylation of Cys-25. N and C termini of AcrA form two , β1 (54-61) and β14 (292-297) lies proximal to inner membrane. A 28 flexible residues connects acylated Cys-25 with the β-barrel domain and allow the protein to reach the periplasmic top of AcrB [7]. A (222-230) located between β-10 (in red)(211-218) and β-11 (in blue) (242-247) closes off the end of the β-barrel near the C-terminus of AcrA fragment. Approximately 100 residues in the C-terminal are predicted to be important for AcrAB-TolC interaction. Structure has been resolved for homologous protein MexA from P. aeruginosa, where similar conclusions on the role of N and C disordered domains in interaction with MexB has been predicted [8]. This segment contains 12 highly conserved amino acid residues viz. P309, V313, V332, R335, G352, L353, G356, D357, V359, V360, G363 and V373. G363 is found to be important for maintaining multidrug resistance property of the efflux system. Substitution of G363 by Cysteine (G363C), prevents appropriate assembly of the tripartite complex [9]

