Chromatin, in eukaryotes, is a very compact structure mainly due to the electrostatic interaction between DNA and histones [1]. This interaction happens because DNA carries an overall negative charge and the histones carry a positive charge when deacetylated. In order to carry out the basic functions, such as transcription and replication, the chromatin has to be decondensed so that enzymes and transcription factors can access the DNA. The decondensation is mainly carried out by the acetylation of a lysine residue on the histone tail by Histone Acetyl Transferases (HATs). This then neutralizes its positive charge. The removal of the acetyl group is carried out by different enzyme family the histone deacetylases (HDACs).

Fig. 1 Acetylation and deacetylation of the lysine residue by HATs and HDACs, respectively.
Function
HDAC8 contains a nuclear localization signal (NLS) at the center of the catalytic domain, and because of this tag it is found in the nucleus, however, it has been reported that HDAC8 has a cytosolic localization in muscle cells [2]. Global deletion of HDAC8 in mice leads to prenatal death due to instability of the skull [3]. HDACs seem to serve an important function in learning, memory and cognition in humans [4].
Disease
HDAC8 is a part of the class I HDAC isozymes. This class is involved in expression of p21, a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor [5]. The p21 proteins main job is to inhibit uncontrolled cell proliferation. A mutation in p53 gene has been reported in many cancer patients [6]. HDAC8 regulates the expression of both the wild type and the mutant form of p53 [6].Inhibition of HDACs provides an anticancer effect [7]. However, a pan-HDAC inhibitor usually shows considerable side effects in a clinical setting. This is probably because multiple HDAC isozymes are involved in several vital cellular processes. Isozyme selective inhibitors are likely to have fewer side effects as compared to a pan-inhibitor. They induce growth inhibition, dedifferentiation, and even cell death in cancer cells [8]. It is widely known that a pan-HDAC inhibitor significantly affects the acetylation status of histones as well as several non-histone proteins, such as HSP90, p53 and others. The therapeutic potential of an HDAC8 selective activator for the treatment of various forms of cancers has recently emerged. In the above case the expression of the tumor suppressor protein (p53) is reportedly suppressed by HDAC8 [6].
In some cases of
Cornelia de Lange syndrome (CLdS), the cohesion acetylation cycle is impaired due to mutations in HDAC8
[9]. The enzyme activity of all Class I HDACs has been found to be reduced in
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
[10]. Therapeutic potential of class I HDAC activators, specifically toward HDAC8, have not been well understood so far. However, there are several human diseases where an HDAC activator could be of great therapeutic benefits. In COPD and CLdS where the HDAC enzyme activity has been reported to be reduced, HDAC activators have a potential to lessen the disease conditions
[9].
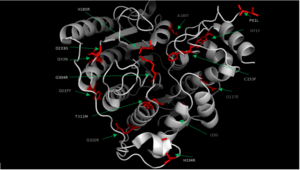
Fig. 2 Various mutations of HDAC8 found in CdLS patients.
Structural highlights
HDAC8 was the first among the HDAC isozymes whose crystal structure became available. The image shows the ribbon structure of . HDAC8 contains a single α/β-deacetylase domain consisting of and an .
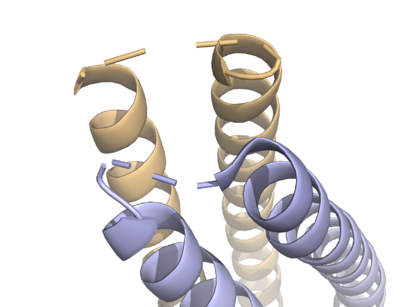
Fig. 3 The various loops associated with HDAC8.
Multiple loops, which emanate from the protein core, play a significant role in maintaining the appropriate geometry of the catalytic pocket. The α/β-fold of the above kind was first observed in a metalloenzyme,
Arginase. The active site of HDAC8 contains a tubular cavity leading to catalytic machinery at the end. The with a square pyramidal geometry. The residues His 180, Asp 267 and Asp 178 occupy the three co-ordination sites, whereas the hydroxamate moiety of SAHA occupies the remaining two sites. In addition, the carbonyl oxygen of the hydroxamate moiety forms a hydrogen bond with Tyr 306. In the absence of any ligand (substrate/inhibitors), two water molecules are bound to the Zn
2+ ion. , which forms a . Notably, the above residues involved in the inhibitor/substrate binding, as well as the catalysis, have been found to be conserved during the course of evolution among class I HDACs. Notably, the carbonyl oxygen of the acetyl-lysine substrate forms a hydrogen bond with the hydroxyl moiety of Y306.
Aside from the catalytic Zn2+ ion, the enzyme activity of HDAC8 is dependent on the presence of the monovalent ion, K+/Na+ [11]. The crystal structure of HDAC8 shows the presence of two binding sites for K+/Na+ [12]. The is located in the vicinity of the enzyme catalytic machinery, and it is hexacoordinated (octahedral geometry) with His 180 (carbonyl oxygen of the main chain), Asp 178 (oxygen atom of the main chain and side chain), Leu 200 (carbonyl oxygen of the main chain), and Ser 199 (O). Notably, His 180 and Asp 178 are the common residues coordinated with both the catalytic Zn2+ as well as the K+/Na+ ion. The is located near the surface. It is hexacoordinated (octahedral geometry) with F189, T192, V195, Y225 as well as two water molecule.
The crystal structure of shows that aspartate residue is important in the substrate binding [13]. The Asp 101 carboxylate moiety makes two consecutive hydrogen bonds with the backbone of the deacetylated peptide substrate. Mutation of Asp 101 to Ala inhibits HDAC8 activity. The Asp residue has been found to be strictly conserved among different HDAC isozymes.
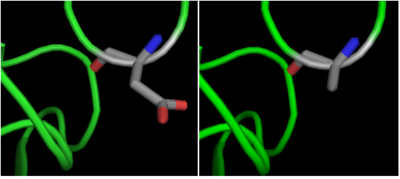
Fig. 4 Mutation of Asp 101 to Ala inhibits HDAC8 activity.
Based on the crystallographic studies, a mechanism of the HDAC8 catalyzed reaction has been proposed.
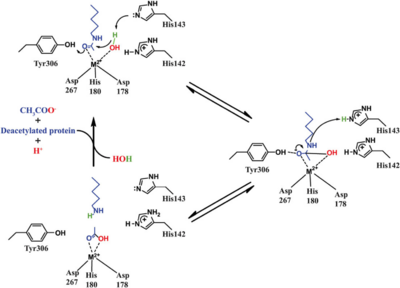
Fig. 5 Catalytic mechanism of HDAC8.
HDAC8 has a some structural features which make it different from other HDACs. It lacks the C-terminal sequence the others use to recruit cofactors [14]. The studies of HDAC8 with different hydroxamate inhibitors: , and shows that there is a certain amount of flexibility in its active site pocket. This seems to be due to the presence of the [14].





