Generalities
The structure is found in the human psoriasin, also called S100A7. This protein belongs to the family of S100 proteins which are involed in the skin celle division and differenciation. They are called like this because of their solubility in a saturated solution with ammonium sulfate at neutral pH [1]. It is a family of 21 proteins of low molecular weights with a high frequence of homologous sequence (often between 40% and 50%). Those proteins are found in cells as homo and heterodimers. Each monomer have a similar structure, beginning with the N-terminal EF Hand and the four-turn which leads to a . Then, there is the three-turn , the two-turn and finally the five-turn . One of their main properties is their ability to bind the calcium. They share some common structures such as two helix-loop-helix structures which are calcium-binding domains more specifically the loop from . All the S100 proteins have different functions in many various cell types. They have significant roles in calcium-associated signal transduction. They play the roles of calcium sensors proteins that regulate the function or distribution of specific target proteins [2].
Human Psoriasin
The protein S100A7 is found in the cytoplasm of keratinocytes and on the chromosome 1q21. S100A7 is highly homologous to S100A15 (koebnerisin) but distinct in expression, tissue distribution and function. The protein has a molecular weight of 23 kDa. The expression of the psoriasin is regulated by different agents. An increase of the cellular amount of calcium also increases the cellular level of S100A7. The UV light increases the expression of the protein. The level of the protein is thought to increase in keratinocytes in response to inflammatory stress. Some studies show that the target protein of the psoriasin could be E-FABP, the epidermal fatty acid binding protein. They proved that E-FABP immobilized on nitrocellulose was able to capture S100A7 and so that those two molecules were probably able to form a complex [3]. Fatty acid binding proteins are involved in cellular transports and in the regulation of the solubility of fatty acids [4]. The biggest difference between the human psoriasin and the rest of the S100 proteins is that the EF-hand at the N-Terminus does not have the ability to bind the calcium [5]. S100A7 also acts as an anti-microbial protein and it is mainly directed against E.Coli. [6].
Disease
Some S100 proteins such as S100A7 are clearly overexpressed in psoriasis, wound healing, skin cancer, inflammation, cellular stress and other skin conditions.
Human psoriasin is highly expressed in hyperproliferative skin conditions such as Atopic_dermatitis and Psoriasis [7] which causes a disruption of the skin barrier. In those conditions, scaling occure frequently on joints, like elbows and knees. Psoriasis is a genetic disease that disrupts cell division in skin cells. In a normal epidermal strcucture, keratinocytes have a regulated process of differentiation. In psoriasis, this differentiation process is disturbed. S100A7 interracts with various signalling proteins and promotes the endothelial cells proliferation. The exact role of the protein in psoriasis has not been found yet but its overexpression is thought to be a cause of the perturbation of the differentiation process of keratinocytes. [8]
The study of S100A7 as well as all of the S100 proteins is therefore of great interest in the search for treatments for epidermal diseases.
Antimicrobial Effect
Human psoriasin can be used as antimicrobial petide against E-coli. Some mutant of S100A7 are capable of decrease the survival rate of E. coli mainly. Mutation of the conserved carboxyl-terminal EF-hand calcium-binding motif or heat denaturation slightly reduces S100A7 antibacterial activity. Because it modify the structure of the protein and reduce the affinity with others molecules [9].
This petide is actually regulated by Caspase-8 using a downregulation of Caspace-8 : mediator of the transcription of the S100A7. This regulation means that less Capase-8 we have more antimicrobial peptide we will get [10]. 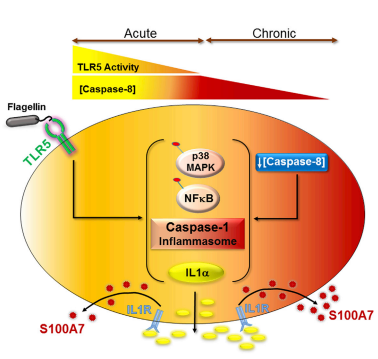
The region between the animo acid is necessery to have a the full antimicrobial effect this amino acid is the central region of S100A7 protein. The others part can be remove without any differencies on the antimicrobial effect.

