This is a default text for your page '. Click above on edit this page' to modify. Be careful with the < and > signs.
You may include any references to papers as in: the use of JSmol in Proteopedia [1] or to the article describing Jmol [2] to the rescue.
Background
G-protein coupled receptors
Function
Structure
transmembrane protein
alpha helix
Class B structural components
As opposed to class A glucagon receptors which have a proline kink, in all secretin-like class B glucagon receptors there is a Glycine at position 393 in Helix VII which allows for a . This Glycine and therefore this helical bend is fully conserved in all secretin-like class B receptors and is an important part of the FQGxxVxxYCF motif.
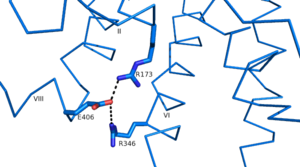
Another important structural component found in all secretin-like class B receptors are the two conserved
salt bridges found between
Arg 346 and
Glu 406 and Arg 173 and Glu 406
.
Since there is no conservation of these residues in class A receptors these salt bridges are likely an important feature of secretin-like class B receptors.
Disulfide bond
As a part of the interface between helices VI, V, and III, a class B specific hydrogen bond occurs between N 318 of Helix V and L 242 of Helix III.
unique components to GPCR
An important interface stabilization interaction between helices I and VII occurs between Ser 152 of Helix I and Ser 390 of Helix VII. Due to their close proximity to one another, they form an important
which serves to stabilize the structure of GCGR.
Clinical Relevance
clinical relevance
References
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644