Sandbox Reserved 1504
From Proteopedia
2N19
Function2N19 is a domain of the polo like protein kinase 4 (PLK4). PLK are eukaryotic regulatory proteins involved in the cell cycle, mainly as a regulator of centriole duplication. These enzymes belong to the family of transferases. They transfer a phosphate group to the side-chain oxygen atom of the serine or threonine residues using ATP as energy. This modification allows activation or inhibition of other proteins. On this PLK4, there is an N-terminal serine-threonine kinase domain as well as a regulatory domain located at the C-terminal end. The latter contains two or three domains called polo box (PB). They are essential since they make it possible to regulate substrate binding, kinase activity and localization.[1] PLK4 is the only polo kinase to have three Polo boxes: PB1, PB2 and PB3. Here, our protein 2n19 corresponds to the PB3.
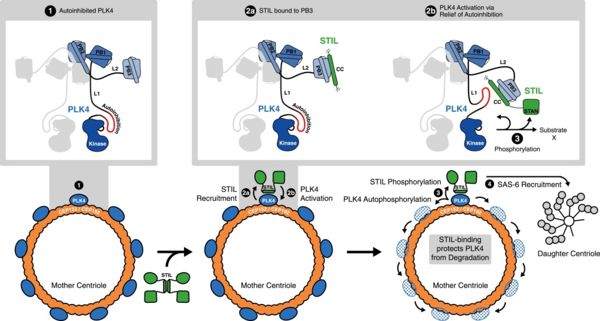
Biological roleLocated in the cytoplasm, the centrosome, consisting of a pair of centrioles, has the major role of being the organizing center of microtubules in animal cells. It is responsible for the formation of the microtubular mitotic spindle during the cell division on which the chromosomes move. They also allow cells to detect chemicals and even move. During cell division, the two centrioles duplicate forming two centrosomes. In order to occur in a suitable way, the duplication needs as many STIL as PLK4 otherwise it leads to deficient cells and thus cancer. We can explain it by the fact that PLK4 recruits STIL, and STIL is phosphorylated by PLK4.
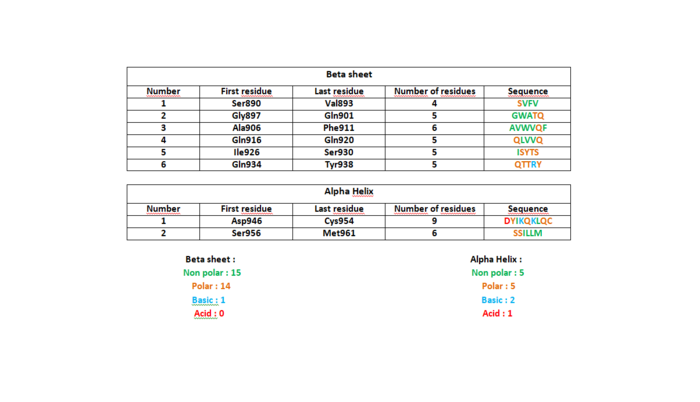
StructurePB3 is an essential domain of PLK4. For a long time unknown, this polo box with a particular shape is essential. Indeed, PB3 role is to target and promote trans autophosphorylation and to limit centriole duplication to once per cell cycle. Human PLK4-PB3 is formed by a single chain of residues 884 to 970 of 88 amino acids. Its theoretical weight is 9,63 kDa. The three-dimensional structure adopted by the protein is perfectly identifiable. There’s six-strand anti-parallel (β1- β6) and a C-terminal alpha on this domain. The following table shows the constitution of amino acids in 2N19 except beta hairpin. The helix is divided in 2 domains: alpha 1 and alpha 2. In this helix we can observe that each amino acid can make at least 3 hydrogen bonds with atoms which are close enough and well disposed. There are almost as many polar and non-polar amino acids especially in beta strands.
Interaction between STIL and 2N19The principle function of 2N19 is thus to get a stronger interaction between PLK4 and STIL, with the help of the 2 others Polo box present in PLK4 too: PB1 and PB2. The purpose is to phosphorylate STIL following the mechanism presented here:
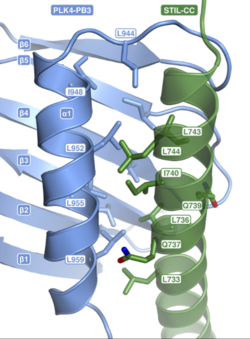
Moreover, when PB3 is bound to STIL-CC (part of STIL), some modifications in its structure happen. Indeed, we have an extension of the first βsheet with the addition of 3 residues, and the alpha helix change its orientation. We have to know notice that there are only monomers in the PLK4, in contrary to its homolog SAK in other eukaryotes. All those changes lead to the recruitment of another protein which is also important in this mechanism : SAS-6.
ConclusionTo conclude, the most important to remind is that 2n19 is the third polo box (PB3) of the enzyme PLK4, a kinase. This enzyme is needed for the centriole duplication (and thus for mitosis…), notably when it interacts with the other protein STIL. The role of 2n19 is to keep a good contact between those 2 proteins and thus to enable the phosphorylation of STIL by PLK4, which will induce the recruitment of other factors. And this will lead to the duplication of centrioles.
ReferencesArquint C, Gabryjonczyk AM, Imseng S, Bohm R, Sauer E, Hiller S, Nigg EA, Maier T. STIL binding to Polo-box 3 of PLK4 regulates centriole duplication. Elife. 2015 Jul 18;4. doi: 10.7554/eLife.07888 | ||||||||||||